Inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of basic trigonometric functions. In mathematics, inverse trigonometric functions are also known as arcus functions or anti-trigonometric functions. The inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of basic trigonometric functions, i.e., sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. It is used to find the angles with any trigonometric ratio. Inverse trigonometric functions are generally used in fields like geometry, engineering, etc.
Table of Contents
What are Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
Inverse trigonometric functions are the trigonometric functions that are used for finding the inverse of the basic trigonometric functions. They are also called “Arc Functions” as for the given value trigonometric functions, they find the length of arc needed to obtain that particular value.
They perform the inverse operation to basic trigonometric functions i.e.
If sin (x) = a ⇒ x = sin-1(a)
Also, In general, sin-1[sin(x)] = x
We write inverse trigonometric functions as sin-1 x, cos-1 x, tan-1 x, cot-1 x, cosec-1 x, and sec-1 x which are inverse functions of sin x, cos x, tan x, cot x, cosec x, and sec x respectively.
Let’s discuss each inverse trigonometric function in detail in this article.
Inverse Trigonometric Function Formulas
There are various inverse trigonometric formulas used some of the important inverse trigonometric formulas are,
Formulas for Negative Functions
The table below discusses the inverse trigonometric function formulas for negative functions.
| Inverse Trig Functions | Formulas |
|---|---|
| Arcsine | sin-1(-x) = -sin-1(x), x ∈ [-1, 1] |
| Arccosine | cos-1(-x) = π -cos-1(x), x ∈ [-1, 1] |
| Arctangent | tan-1(-x) = -tan-1(x), x ∈ R |
| Arccotangent | cot-1(-x) = π – cot-1(x), x ∈ R |
| Arcsecant | sec-1(-x) = π -sec-1(x), |x| ≥ 1 |
| Arccosecant | cosec-1(-x) = -cosec-1(x), |x| ≥ 1 |
Formulas for Reciprocal Functions
The inverse trigonometric function for reciprocal values of x converts the given inverse trigonometric function into its reciprocal function. This follows from the trigonometric functions where sin and cosecant are reciprocal to each other, tangent and cotangent are reciprocal to each other, and cos and secant are reciprocal to each other.
The inverse trigonometric formula of inverse sine, inverse cosine, and inverse tangent are expressed as,
- sin-1x = cosec-11/x, x ∈ R – (-1, 1)
- cos-1x = sec-11/x, x ∈ R – (-1, 1)
- tan-1x = cot-11/x, x > 0
Formulas for Complementary Functions
Complementary functions are the functions whose addition results in right angles. Thus, the sum of the complementary inverse trigonometric functions also results in a right angle.
The complementary function pairs are, sine-cosine, tangent-cotangent, and secant-cosecant i.e. for a similar function the sum of these functions results in the right angle. Various inverse trigonometric complementary functions are,
- sin-1x + cos-1x = π/2, x ∈ [-1,1]
- tan-1x + cot-1x = π/2, x ∈ R
- sec-1x + cosec-1x = π/2, x ∈ R – [-1,1]
Sum and Difference of Inverse Trigonometric Function Formulas
Sum and difference of two inverse trigonometric functions can be combined to form a single inverse function, as per the below set of formulas. The sum and the difference of the inverse trigonometric functions have been derived from the trigonometric function formulas of sin (A + B), cos (A + B), and tan (A + B). These inverse trigonometric function formulas can be used to further derive the double and triple function formulas.
- sin-1x + sin-1y = sin-1(x.√(1 – y2) + y√(1 – x2))
- sin-1x – sin-1y = sin-1(x.√(1 – y2) – y√(1 – x2))
- cos-1x + cos-1y = cos-1(xy – √(1 – x2).√(1 – y2))
- cos-1x – cos-1y = cos-1(xy + √(1 – x2).√(1 – y2))
- tan-1x + tan-1y = tan-1(x + y)/(1 – xy), if xy < 1
- tan-1x + tan-1y = tan-1(x – y)/(1 + xy), if xy > – 1
Double Inverse Trigonometric Function Formulas
Double inverse trigonometric function formulas are the formulas that give the values of the double angle in the inverse trigonometric function. Some important double inverse trigonometric function formulas are,
- 2sin-1x = sin-1(2x.√(1 – x2))
- 2cos-1x = cos-1(2x2 – 1)
- 2tan-1x = tan-1(2x/1 – x2)
These formulas are derived using the basic double-angle formulas of the trigonometric function.
Triple of Inverse Trigonometric Function Formulas
Triple inverse trigonometric function formulas are the formulas that give the values of the triple angle in the inverse trigonometric function. Some important triple inverse trigonometric function formulas are,
- 3sin-1x = sin-1(3x – 4x3)
- 3cos-1x = cos-1(4x3 – 3x)
- 3tan-1x = tan-1(3x – x3/1 – 3x2)
These formulas are derived using the basic triple-angle formulas of the trigonometric function.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Domain and Range
The domain and the range of the inverse trigonometric function are added in the table below.
| Function | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
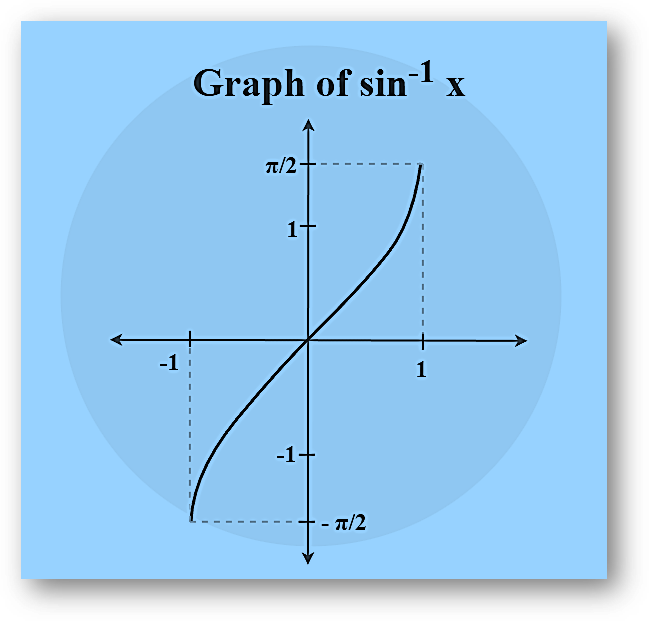
| y = sin-1 x | [-1, 1] | [-π/2, π/2] |
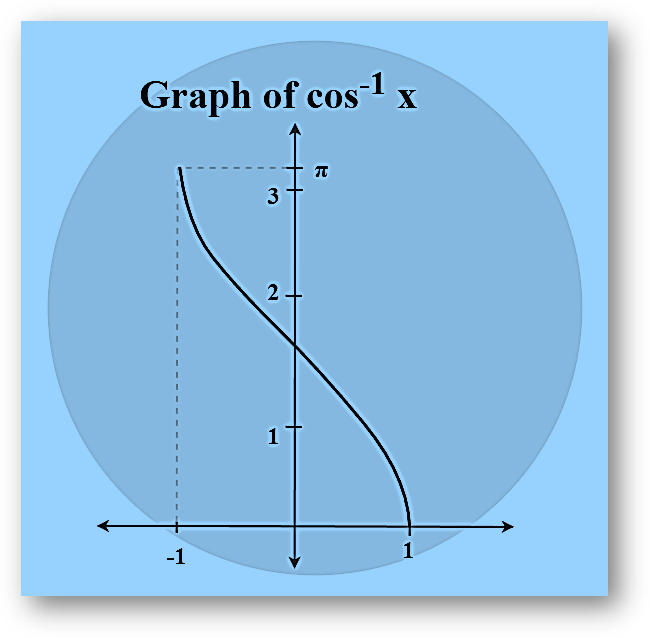
| y = cos-1 x | [-1, 1] | [0 , π] |
| y = cosec-1 x | R – (-1,1 ) | [-π/2, π/2] – {0} |
| y = sec-1 x | R – (-1, 1) | [0 , π] – {π/2} |
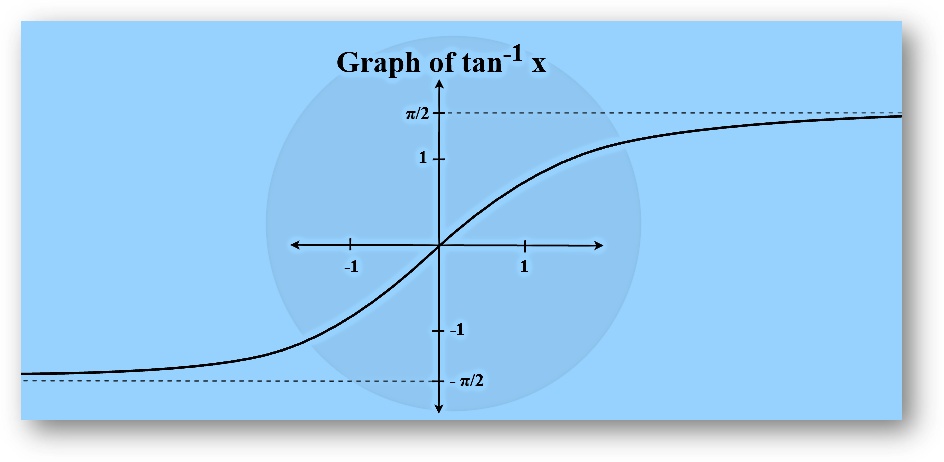
| y = tan-1 x | R | (-π/2, π/2) |
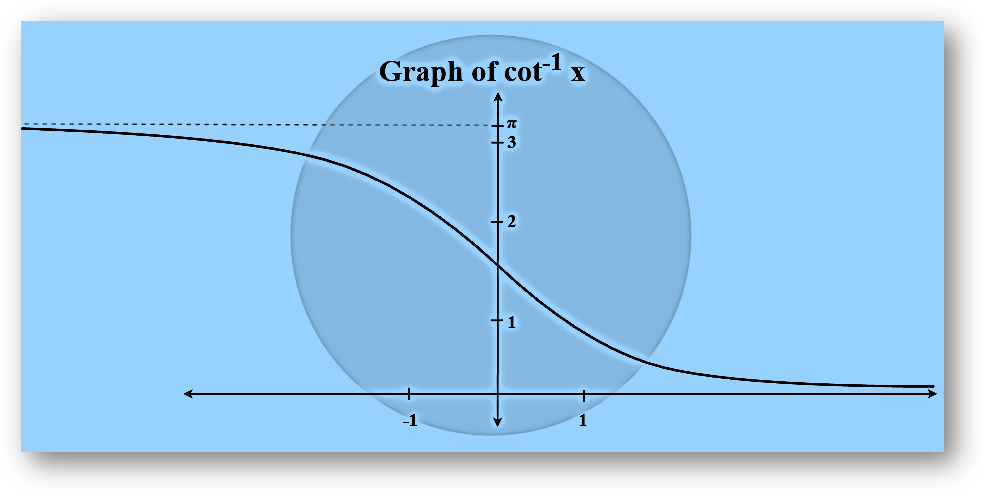
| y = cot-1 x | R | (0 , π) |
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Formulas PDF
There are various inverse trigonometric formulas used in complex problems. Download the pdf below for all the important Inverse Trigonometric formulas.
Inverse Trigonometric Function Types
There are a total of six Inverse Trigonometric Functions that are,
- Arcsine Function
- Arccosine Function
- Arctangent Function
- Arccotangent Function
- Arcsecant Function
- Arccosecant Function
Arcsine Function
Arcsine function is an inverse of the sine function denoted by sin-1x. It returns the angle whose sine corresponds to the provided number.
sin θ = (Opposite/Hypotenuse)
=> sin-1 (Opposite/Hypotenuse) = θ
Example: sin-1(1/2) = π/6
Theorem of sin inverse is: d/dx sin-1x = 1/√(1 – x2)
Proof:
sin(θ) = x
Now,
f(x) = sin-1x ..(eq1)
substitute value of sin in eq(1)
f(sin(θ)) = θ
f'(sin(θ))cos(θ) = 1 .. differentiating equation
we know that,
sin2θ + cos2θ= 1
So, cos = √(1 – x2)
f'(x) = 1/√(1 – x2)
Now,
d/dx sin-1x = 1/√(1 – x2)
Hence Proved.
Arccosine Function
Arccosine function is an inverse of the sine function denoted by cos-1. It returns the angle whose cosine corresponds to the provided number.
cos θ = (Hypotenuse/Adjacent)
=> cos-1 (Hypotenuse/Adjacent) = θ
Example: cos-1(1/2) = π/3
Theorem of cos inverse is: d/dx cos-1(x) = -1/√(1 – x2)
Proof:
cos(θ) = x
θ = arccos(x)
dx = dcos(θ) = −sin(θ)dθ .. differentiate the equation
Now,
we know that,
sin2 + cos2 = 1
So, cos = √(1 – x2)
−sin(θ) = −sin(arccos(x)) = -√(1 – x2)
dθ/dx = −1/sin(θ) = -1/√(1 – x2)
So,
dθ/dx cos-1(x) = -1/√(1 – x2)
Hence Proved.
Arctangent Function
Arctangent function is an inverse of the tangent function denoted by tan-1. It returns the angle whose tangent corresponds to the provided number.
tan θ = (Opposite/Adjacent)
=> tan-1 (Opposite/Adjacent) = θ
Example: tan-1(1) = π/4
Theorem of tan inverse is: d/dx tan-1(x) = 1/(1 + x2)
Proof:
tan(θ) = x
θ = arctan(x)
We know that,
tan2θ + 1 = sec2θ
dx/dθ = sec2y .. differentiating tan function
dx/dθ = 1+x2
Therefore,
dθ/dx = 1/(1 + x2)
Hence Proved.
Arccotangent Function
Arccotangent function is an inverse of the tangent function denoted by cot-1. It returns the angle whose tangent corresponds to the provided number.
cot θ = (Adjacent/Opposite)
=> cot-1 (Adjacent/opposite) = θ
Example: cot-1(1) = π/4
Arcsecant Function
Arcsecant function is an inverse of the secant function denoted by sec-1. It returns the angle whose secant corresponds to the provided number.
sec θ = (Base/Hypotenuse)
=> sec-1 (Base/Hypotenuse) = θ
Example: sec-1(2) = π/3
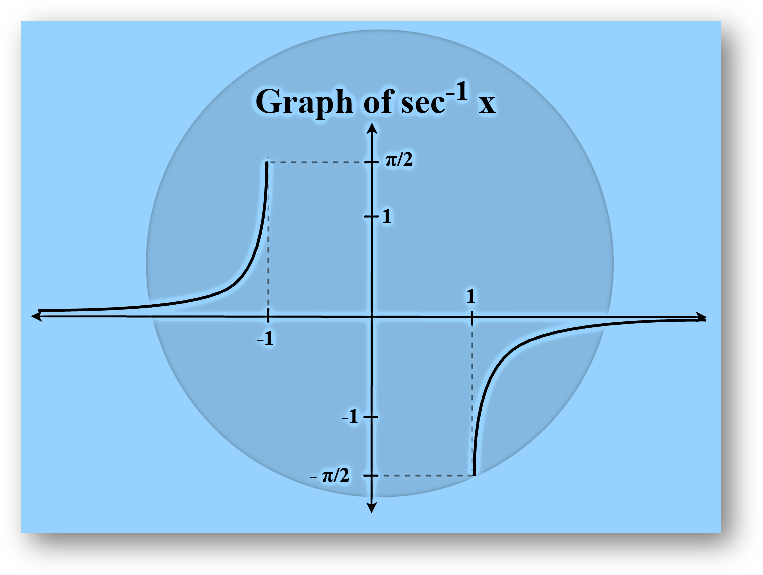
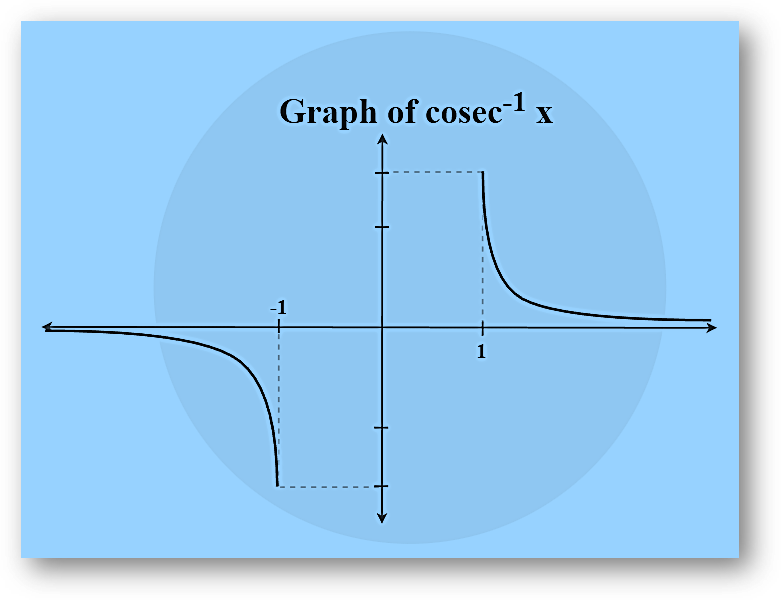
Arccosecant Function
Arccosecant function is an inverse of the cosecant function denoted by cosec-1. It returns the angle whose cosecant corresponds to the provided number.
cosec θ = (Adjacent/Hypotenuse)
=> Cossec-1 (Adjacent/Hypotenuse) = θ
Example: Cosec-1(2) = π/6
Restricting Domains of Functions to Make Them Invertible
A real function in the range ƒ: R ⇒ [-1, 1] defined by ƒ(x) = sin(x) is not a bijection since different images have the same image such as ƒ(0) = 0, ƒ(2π) = 0,ƒ(π) = 0, so, ƒ is not one-one. Since ƒ is not a bijection (because it is not one-one) therefore inverse does not exist. To make a function bijective we can restrict the domain of the function to [−π/2, π/2] or [−π/2, 3π/2] or [−3π/2, 5π/2] after restriction of domain ƒ(x) = sin(x) is a bijection, therefore ƒ is invertible. i.e. to make sin(x) we can restrict it to the domain [−π/2, π/2] or [−π/2, 3π/2] or [−3π/2, 5π/2] or……. but [−π/2, π/2] is the Principal solution of sinθ, hence to make sinθ invertible. Naturally, the domain [−π/2, π/2] should be considered if no other domain is mentioned.
- ƒ:[−π/2, π/2] ⇒ [-1 , 1] is defined as ƒ(x) = sin(x) and is a bijection, hence inverse exists. The inverse of sin-1 is also called arcsine and inverse functions are also called arc functions.
- ƒ:[−π/2 , π/2] ⇒ [−1 , 1] is defined as sinθ = x ⇔ sin-1(x) = θ , θ belongs to [−π/2 , π/2] and x belongs to [−1 , 1].
Similarly, we restrict the domains of cos, tan, cot, sec, and cosec so that they are invertible.
Domain & Range of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The domain and the range of the inverse trigonometric function are added in the table below.
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
We can find the differentiation of inverse trigonometric functions using differentiation formulas. The image added below shows the same
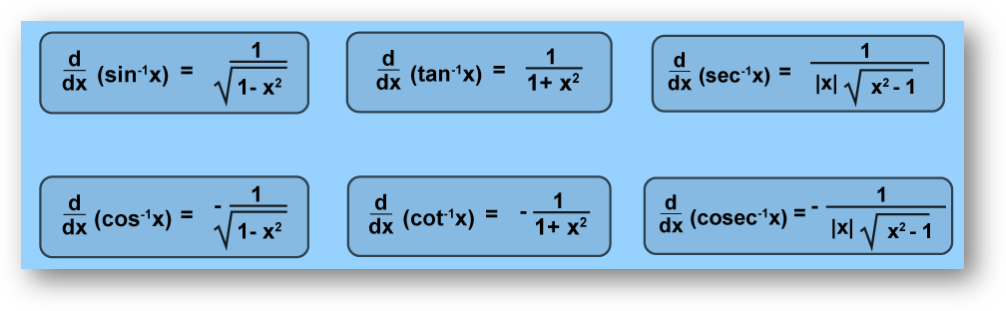
The following table gives the result of the differentiation of inverse trig functions.
| Inverse Trigonometric Functions | dy/dx |
|---|---|
| y = sin 1(x), x ≠ -1, +1 | 1/√(1-x2) |
| y = cos 1(x), x ≠ -1, +1 | -1/√(1-x2) |
| y = tan-1(x), x ≠ -i, +i | 1/(1+x2) |
| y = cot-1(x), x ≠ -i, +i | -1/(1+x2) |
| y = sec 1(x), |x| > 1 | 1/[|x|√(x2-1)] |
| y = cosec 1(x), |x| > 1 | -1/[|x|√(x2-1)] |
Integrals of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Here are the integral formulas of inverse trigonometric functions. To see how to derive each one of them,
| Inverse Trigonometric Function | Integral |
|---|---|
| ∫ sin-1x dx | x sin-1x + √ (1 – x²) + C |
| ∫ cos-1x dx | x cos-1x – √ (1 – x²) + C |
| ∫ tan-1x dx | x tan-1x – (1/2) ln |1 + x²| + C |
| ∫ csc-1x dx | x csc-1x + ln |x + √ (x² – 1)| + C |
| ∫ sec-1x dx | x sec-1x – ln |x + √ (x² – 1) | + C |
| ∫ cot-1x dx | x cot-1x + (1/2) ln |1 + x²| + C |
Examples on Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Example 1: Find x, if sin(x) = 1/2
Solution:
Given, sin x = 1/2
Using inverse trigonometric function formulas,
x = sin-1(1/2)
Using Trigonometric Table
x = sin-1[sin(π/6)]
x = π/6
Thus, the required value of x is π/6
Example 2: Find the value of cos-1(1/2) – sec-1(-2).
Solution:
cos-1 (1/2) – sec-1(-2)
= π/3 – (π – sec-12)
Using Trigonometric Table
= π/3 – (π – π/3)
= π/3 – π + π/3
= π/3 + π/3 – π
= 2π/3 – π
= -π/3
Thus, the required value of the given expression is -π/3
Example 3: Find cos [cos-1 (11/15)]
Solution:
= cos [cos-1 (11/15)]
We know that, cos [cos-1 (x)] = x
= 11/15
Example 4: Find the value of cot-1(1) + sin-1(-1/2) + sin-1(1/2).
Solution:
Using inverse trigonometric functions formulas,
= cot-1(1) + sin-1(-1/2) + sin-1(1/2)
= cot-1(1) – sin-1(1/2) + sin-1(1/2)
= cot-1(1)
= π/4
Thus, the required solution is π/4
Example 5: Simplify sin(tan-1x)
Solution:
Taking sin2 (θ) + cos2 (θ) = 1
dividing both sides by sin2(θ)
1 + cot2 (θ) = cosec2 (θ)
1 + 1/tan2 (θ) = 1/sin2 (θ)
(tan2 (θ) + 1)/tan2 (θ) = 1/sin2 (θ)
Taking the inverse
sin2 (θ) = tan2 (θ)/(tan2 (θ) + 1)…(1)
taking θ = tan-1(x) In eq (1)
sin2 (tan-1(x)) = tan2 (tan-1(x))/(tan2 (tan-1(x)) + 1)
We know that, tan (tan-1(x)) = x
sin2 (tan-1(x)) = x2 / x2 + 1
Taking square root on both sides,
sin (tan-1(x)) = x / √(x2 + 1)
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12
Inverse Trigonometric Functions is a key topic in the Class 12 mathematics curriculum, typically covered in Chapter 2. It deals with the inverse of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent, and is important for calculus, integration, and solving trigonometric equations.
Conclusion
Inverse trigonometric functions are essential tools in mathematics and science, allowing us to determine angles from known trigonometric values.These functions include arcsin(x), arccosecant(x), arcsec(x) and arctan(x) among others, each with specific domains and ranges. They are crucial for solving equations involving angles, modeling periodic phenomena, and applications in fields like geometry, physics, and engineering.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions – FAQs
How to Find the Inverse of Trigonometric Functions?
Inverse Trigonometric functions can easily be found using the basic trigonometric function as,If sin x = y then the inverse sin function sin-1 y can easily be calculated as,
x = sin-1 y
How to use Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
Inverse Trigonometric functions are used to find the inverse of the basic trigonometric functions they are widely used to solve complex problems of Trigonometry, SHM, and others.
What are Inverse Trigonometric Function Identities for Reciprocal Functions?
The inverse trigonometric formula of reciprocal functions, inverse sine, inverse cosine, and inverse tangent are,
- sin-1x = cosec-11/x, x ∈ R – (-1, 1)
- cos-1x = sec-11/x, x ∈ R – (-1, 1)
- tan-1x = cot-11/x, x > 0
How many Trigonometric Identities are there?
There are three basic trigonometric identities,
- sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1
- 1+tan2 θ = sec2 θ
- cosec2 θ = 1 + cot2 θ
What are the 6 Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
The six inverse trigonometric functions are,
- sin-1 x
- cos-1 x
- tan-1 x
- cot-1 x
- cosec-1 x
- sec-1 x
What is the Range and Domain of Inverse Sine Trigonometric Function?
We write the inverse sine function as sin-1(x) or arcsin (x). The domain and range of Inverse Sine Function are,
- Domain of Inverse Sine Trigonometric Function: [-1, 1]
- Range of Inverse Sine Trigonometric Function: [0, π]
What is the Range and Domain of arccosecant Function?
We write the arccosecant function as cosec-1(x) or arccosecant(x). The domain and range of Inverse cosecant Function are,
- Domain of Inverse cosecant Trigonometric Function: (−∞,−1] ∪ [1,∞)
- Range of Inverse Sine Trigonometric Function: [−2π,0)∪(0,2π]


