Anand Classes provides well-explained notes on Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds for Class 11 Chemistry. Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the arrangement of valence electrons in molecules. In the case of multiple covalent bonds (double and triple bonds), shared electron pairs are represented by two or three lines respectively, as in molecules like $O_2$, $CO_2$, and $N_2$. These notes also include MCQs, solved examples, and practice questions tailored for board exams, JEE, and NEET. Click the print button to download the complete study material and notes in PDF format.
Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds
If the normal valence of an atom is not satisfied by sharing a single electron pair between atoms, the atoms may share more than one electron pair between them.
Types of Covalent Bonds
- Single Covalent Bond ($-$)
If two atoms share one electron pair, the bond is called a single covalent bond and is represented by one dash ($-$).
Example: $H_2$, $Cl_2$, $CH$$_4$ - Double Covalent Bond ($=$)
If two atoms share two electron pairs, the bond is called a double covalent bond and is represented by two dashes ($=$).
Example: $O_2$, $CO$$_2$, $C$$_2$H$_4$ (ethylene). - Triple Covalent Bond ($equiv$)
If two atoms share three electron pairs, the bond is called a triple covalent bond and is represented by three dashes ($\equiv$).
Example: $N_2$, $C$$_2$$H$$_2$ (acetylene).
Examples of Molecules with Multiple Bonds
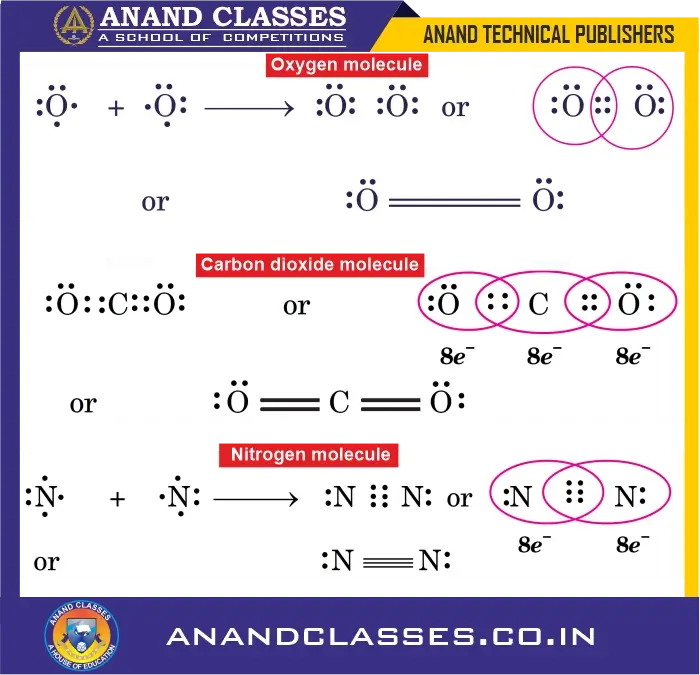
1. Oxygen Molecule ($O_2$)
- Each oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons and requires 2 electrons to complete its octet.
- Each oxygen contributes 2 electrons for sharing, forming a double bond.
O = O
2. Carbon Dioxide ($CO_2$)
- Carbon has 4 valence electrons and each oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
- Carbon shares 2 electrons with each oxygen, forming two double bonds.
O = C = O
3. Nitrogen Molecule ($N_2$)
- Each nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons and needs 3 more to complete its octet.
- Both atoms share three electron pairs, forming a triple bond.
N ≡ N
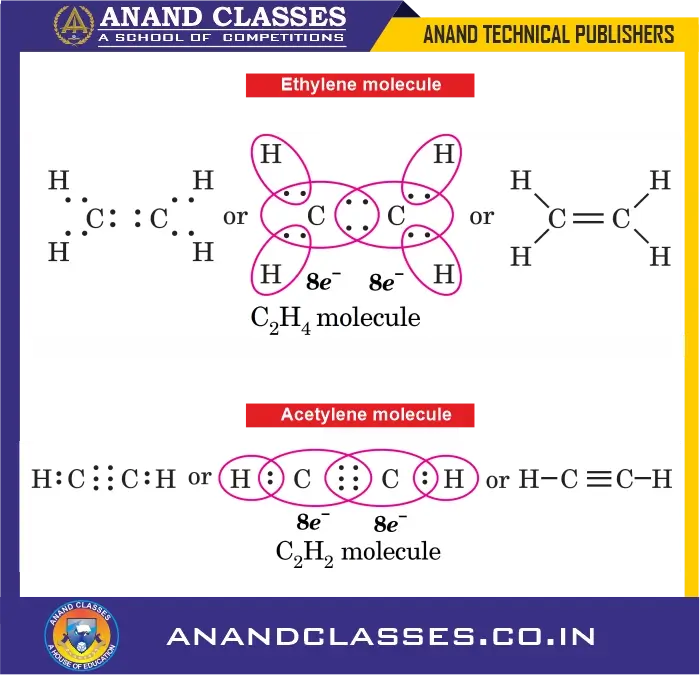
4. Ethylene ($C_2H_4$)
- Each carbon atom shares two electrons with two hydrogen atoms and two electrons with the second carbon atom.
- A double bond exists between the two carbon atoms.
H2C = CH2
5. Acetylene ($C_2H_2$)
- Each carbon atom shares one electron with one hydrogen atom and three electrons with the other carbon atom.
- A triple bond exists between the two carbon atoms.
HC ≡ CH
Key Points
- Single bond: sharing of one electron pair ($-$).
- Double bond: sharing of two electron pairs ($=$).
- Triple bond: sharing of three electron pairs ($\equiv$).
- Bond strength and length:
- Triple bond is strongest and shortest.
- Double bond is intermediate.
- Single bond is weakest and longest.
Short Answer Conceptual Types Questions (SAT) on Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds
Q1. What is a multiple covalent bond?
A. A bond formed when two atoms share more than one electron pair (double or triple bond) to achieve stable configurations.
Q2. How is a double bond represented in a Lewis structure?
A. By two dashes ($=$) or two shared electron pairs between atoms.
Q3. Which bond is stronger and shorter: single, double, or triple?
A. Triple bond ($\equiv$) is the strongest and shortest.
Q4. Give one example each of a double and a triple bond.
A. Double bond: $O_2$, $CO_2$, $C_2H_4$.
Triple bond: $N_2$, $C_2H_2$.
Q5. Why do atoms form multiple bonds instead of single bonds?
A. When the octet rule cannot be satisfied by sharing only one electron pair, atoms share two or three pairs to complete their octets.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) With Answers and Explanation on Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds
1. The number of shared electron pairs in $O_2$ is:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: B. 2 (double bond)
2. Which of the following molecules contains a triple covalent bond?
A. $CO_2$
B. $C_2H_4$
C. $N_2$
D. $O_3$
Answer: C. N$_2$
3. The correct Lewis structure of $CO_2$ contains:
A. Two single bonds
B. One single and one double bond
C. Two double bonds
D. One triple bond
Answer: C. Two double bonds
4. Which statement about bond length is correct?
A. Single bond < Double bond < Triple bond
B. Triple bond < Double bond < Single bond
C. Double bond < Triple bond < Single bond
D. Single bond = Double bond = Triple bond
Answer: B. Triple bond < Double bond < Single bond
5. In acetylene ($C_2H_2$), each carbon atom is bonded to:
A. Two hydrogens and one carbon by single bonds
B. One hydrogen and one carbon by a triple bond
C. Two hydrogens and one carbon by a double bond
D. One hydrogen and one carbon by a double bond
Answer: B. One hydrogen and one carbon by a triple bond
Assertion Reason Type Questions With Answers and Explanation on Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds
Assertion (A): Triple bonds are shorter and stronger than double bonds.
Reason (R): Sharing of three electron pairs increases the electron density between the nuclei.
- (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- (B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- (C) A is true, R is false.
- (D) A is false, R is true.
Answer: A
Assertion (A): Carbon in CO$_2$ forms a single bond with each oxygen.
Reason (R): Carbon requires only two electron pairs to complete its octet.
- (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- (B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- (C) A is true, R is false.
- (D) A is false, R is true.
Answer: D (Carbon forms two double bonds, not single bonds)
Case Study based on Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Covalent Bonds
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions below:
Nitrogen molecule ($N_2$) is one of the most stable diatomic molecules. Each nitrogen atom has five valence electrons. To complete their octets, both nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons, forming a triple bond ($N \equiv N$). The triple bond makes the molecule chemically inert and gives it a very high bond energy.
Questions:
- How many electrons are shared between the two nitrogen atoms?
Answer: Six electrons (three pairs). - Why does $N_2$ have a very high bond energy?
Answer: Due to the presence of a triple bond, which has strong electrostatic attraction. - Predict the bond length trend among $N_2$, $O_2$, and $F_2$.
Answer: $N_2$ < $O_2$ < $F_2$ (triple < double < single bond). - What is the valence of nitrogen in $N_2$?
Answer: Three, because each nitrogen shares three electrons.