Composite Functions
Let f : A->B and g : B->C be two functions. Then the composition of f and g, denoted by g o f, is defined as the function g o f : A->C given by g o f (x) = g{f(x)}, ∀ x ∈ A.
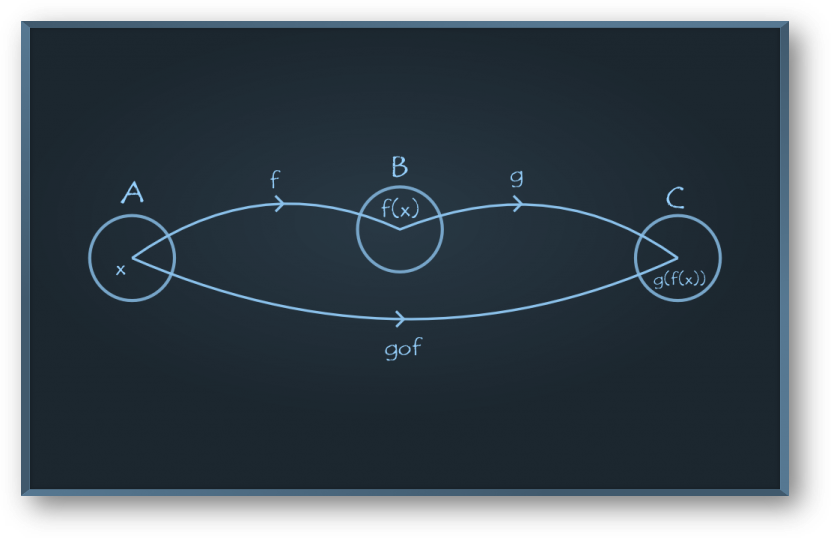
Clearly, dom(g o f) = dom(f).
Also, g o f is defined only when range(f) is a subset of dom(g).
Table of Contents
Evaluating composite functions
We know composite function is written as f o g(x), g o f(x) and so on. Here f o g(x) will be evaluated as f{g(x)} and g o f(x) will be evaluated as g{f(x)}.
Solved Examples
Problem 1: Let f : {2, 3, 4, 5} -> {3, 4, 5, 9} and g : {3, 4, 5, 9} -> {7, 11, 15} be functions defined as
f(2) = 3, f(3) = 4, f(4) = f(5) = 5 and g (3) = g(4) = 7 and g(5) = g(9) = 11. Find g o f(x).
Solution:
g o f(x) = g{ f(x)}. So first we find the inner bracket which is f(x) here.
We have the values of f(2), f(3), f(4) and f(5), hence we have to find the values of g o f(x) for all these values.
g o f(2) = g{ f(2) } = g(3) = 7,
g o f (3) = g{ f(3) } = g(4) = 7,
g o f(4) = g{ f(4) } = g(5) = 11
And g o f(5) = g(5) = 11.
Problem 2: Show that if f : A -> B and g : B -> C are onto, then g o f : A -> C is also onto.
Solution
Given an arbitrary element z ∈ C, there exists a pre-image y of z under g such that g(y) = z, since g is onto.
Further, for y ∈ B, there exists an element x in A with f(x) = y, since f is onto.
Therefore, g o f(x) = g{ f(x) } = g(y) = z, showing that g o f is onto.
Problem 3: Let ƒ: R->R:f(x) = (x2 – 3x + 2). Find f o f(x).
Solution:
f o f(x) = f {f(x) } = f(x2 – 3x + 2) = f(y) (let y = x2 – 3x + 2)
= y2 – 3y + 2
= (x2 – 3x + 2) – 3(x2 – 3x + 2) + 2
= x4 – 6x3 + 10x2 – 3x.
Evaluating Composite Functions: Using Tables
In this type of questions, we will be given a table with values of x, f(x), g(x) and we will need to find the composite of f(x) and g(x) like in example 1 we are asked to find f o g(1).
To find the solution, we will start from the inner bracket and find its value in the table given, so we will find the value of g(1) from the table which is 4. Then for the outer bracket again we will find its value from the given table, so we will find the value of f(4) from the table which is 2. Hence, we will get the required answer which is 2 in this case.
Problem 1: Using the table below, evaluate f o g(1) and g o f(4).
| x | f(x) | g(x) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 8 |
Solution:
So, f o g(1) = f{g(1)} and g o f(4) = g{f(4)}.
We first evaluate the inner bracket then the outer bracket, using the values given in table.
For f{g(1)}, g(1) = 4. Now f(4) = 2.
Hence, f{g(1)} = 2.
Similarly, for g{f(4)}, f(4) = 2. Now g(2) = 8.
Hence, g{f(4)} = 8.
Therefore, f o g(1) = f{g(1)} = f(4) = 2 and g o f(4) = g{f(4)} = g(2) = 8.
Problem 2: Using the table below, evaluate f o g(3) and f o f(1).
| x | f(x) | g(x) |
| 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | 7 | 3 |
| 3 | 8 | 5 |
| 4 | 6 | 7 |
| 5 | 2 | 9 |
Solution:
So, f o g(3) = f{g(3)} and f o f(1) = f{f(1)}.
We first evaluate the inner bracket then the outer bracket, using the values given in table.
For f{g(3)}, g(3) = 5. Now f(5) = 2.
Hence, f{g(3)} = 2.
Similarly, for f{f(1)}, f(1) = 3. Now f(3) = 8.
Hence, f{f(1)} = 8.
Therefore, f o g(3) = f{g(3)} = f(5) = 2 and f o f(1) = f{f(1)} = f(3) = 8.
Evaluating composite functions: Using Graphs
In this type of questions, we will be given a graph having f(x) and g(x) curve, and we will be asked to find a composite of f(x) and g(x) like in example 1 we have to find f o g(2).
Again we will start from the inner bracket, so we have to find g(2). So we will see the g(x) curve. So at x=2, we find that y=3. Now we will need to find f(3). So we will see the f(x) curve. Now we will look at x=3, there we find y=4. Hence, we get the required solution which is 3 in example 1.
Problem 1: Using the graphs below, evaluate f o g(2).
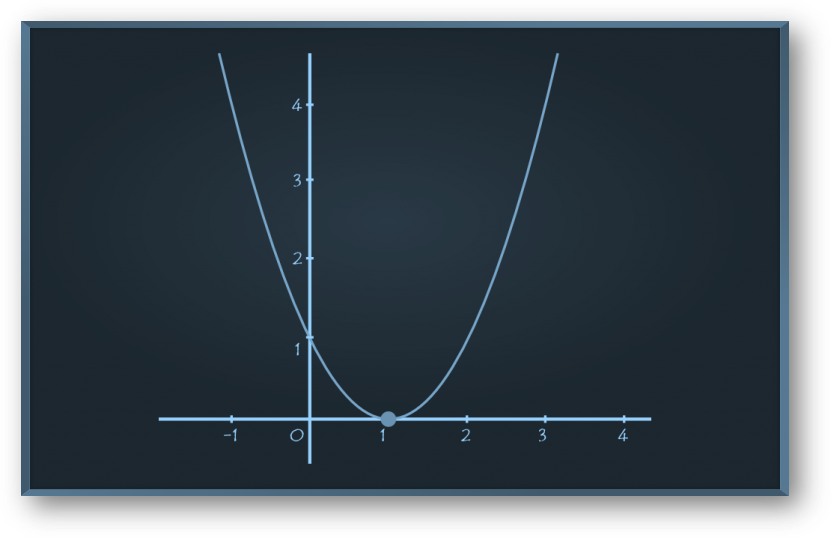
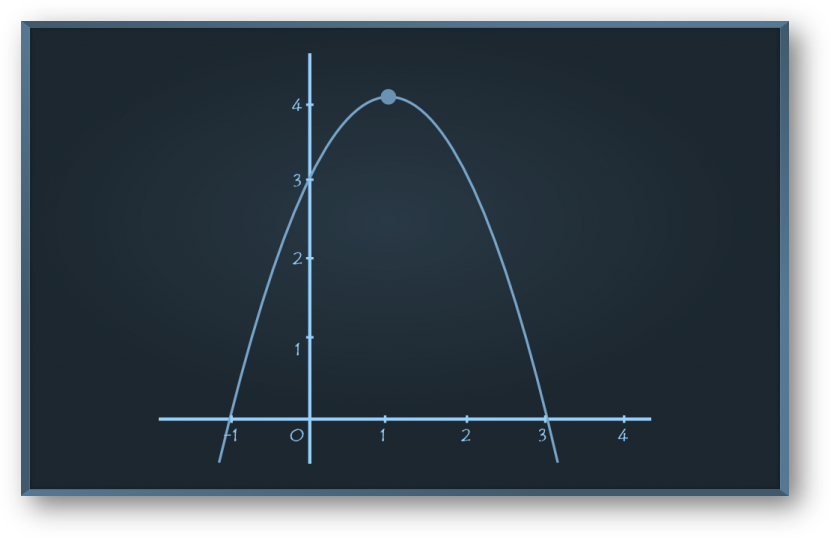
Solution:
So, f o g(2) = f{ g(2) }
From the graph of g(x), we need to find g(2),
when x = 2, y = 3, hence g(2) = 3
Now f o g(2) = f(g(2)) = f(3).
From the graph of f(x), we need to find f(3),
when x = 3, y = 4, hence f(3) = 4
Therefore, f o g(2) = f{g(2)} = f(3) = 4.
Problem 2: Using the graph below, evaluate g o h(5).
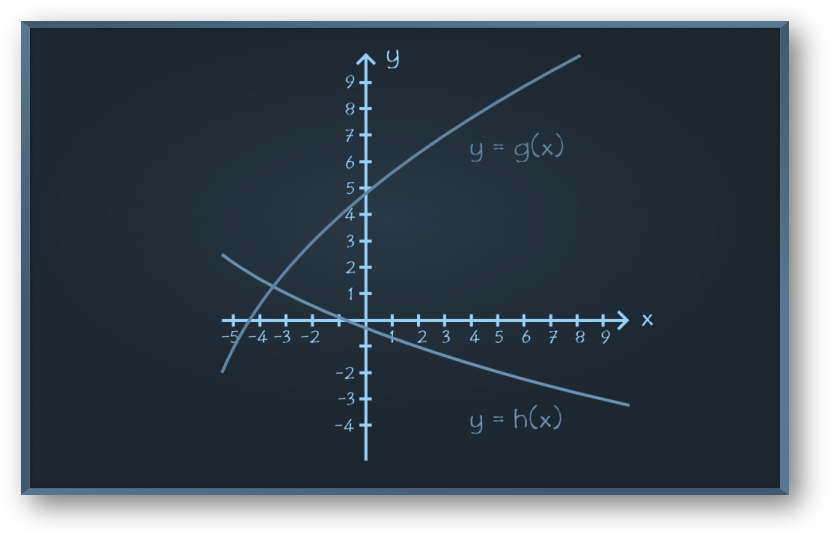
Solution:
So, g o h(5) = g{ h(5) }
From the graph of h(x), we need to find h(5),
When x = 5, y = -2, hence h(5) = -2
Now g o h(5) = g{h(5)} = g(-2).
From the graph of g(x), we need to find g(-2),
when x = -2, y = 3, hence g(-2) = 3
Therefore, g o h(5) = g{h(5)} = g(-2) = 3.


