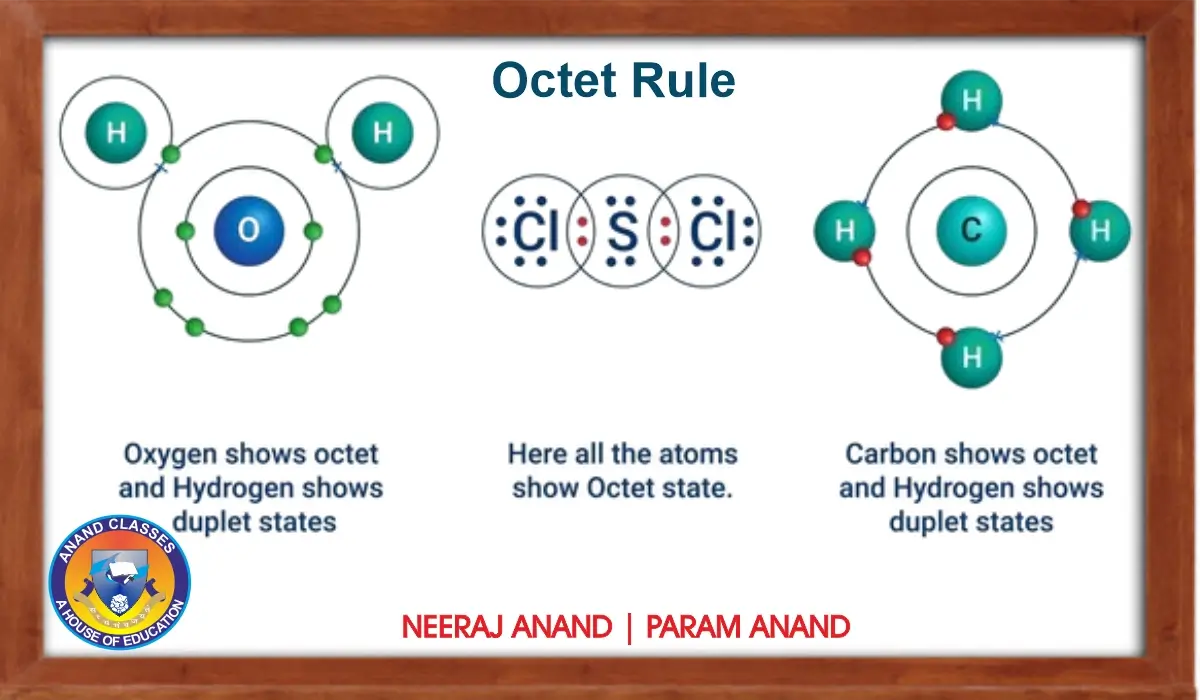
Anand Classes provides detailed Class 11 Chemistry study material for JEE and NEET on the Octet Rule, explaining its theory, significance, and applications in chemical bonding with step-by-step Questions and Answers, solved examples, MCQs, assertion-reason questions, and case study-based problems to build a strong understanding of how atoms achieve stability. Click the print button to download study material and notes.
What is Octet Rule and Modes of Chemical Combination ?
In the light of the octet rule, W. Kossel and G. N. Lewis, in 1916, developed an important theory of chemical combination between atoms known as the electronic theory of chemical bonding.
According to this theory, atoms achieve a stable octet when they are linked by chemical bonds. In other words, atoms combine to have an octet in their valence shells (stable noble gas configurations). They do so either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another (gaining or losing) or by sharing of valence electrons.
Thus, atoms combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another (gaining or losing) or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. This is called the octet rule.
Examples
- Sodium, magnesium, and aluminium in the third period of the periodic table lose electrons with the formation of positive ions (cations) that have the same electronic configuration as neon ($1s^22s^22p^6$).
$$
\mathrm{Na} \;\;\longrightarrow\;\; \mathrm{Na}^+ + e^- \
$$ $$1s^22s^22p^63s^1 \;\;\longrightarrow\:\;\; 1s^22s^22p^6$$
$$
\mathrm{Mg} \;\;\longrightarrow\;\; \mathrm{Mg}^{2+} + 2e^- \
$$ $$1s^22s^22p^63s^2 \;\;\longrightarrow\:\;\; 1s^22s^22p^6$$
$$
\mathrm{Al} \;\;\longrightarrow\;\; \mathrm{Al}^{3+} + 3e^- \
$$ $$1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^1 \;\;\longrightarrow\:\;\; 1s^22s^22p^6$$
- On the other hand, oxygen and fluorine can acquire noble gas configuration by easily gaining electrons to form negative ions (anions).
$$
\mathrm{O} + 2e^- \;\;\longrightarrow\;\; \mathrm{O}^{2-} \
$$ $$1s^22s^22p^4 \;\;\longrightarrow\:\;\; 1s^22s^22p^6$$
$$
\mathrm{F} + e^- \;\;\longrightarrow\;\; \mathrm{F}^- \
$$ $$1s^22s^22p^5 \;\;\longrightarrow\:\;\; 1s^22s^22p^6$$
What are Periodic Table Facts given by W. Kossel ?
In relation to chemical bonding, W. Kossel drew attention to the following facts of the periodic table :
- In the periodic table, the highly electronegative halogens are placed on the right, and the highly electropositive alkali metals are present on the extreme left. These two families are separated by noble gases.
- Halogens gain an electron to form a negative ion, while alkali metals lose an electron to form a positive ion. Therefore, these ions are formed by the gain or loss of electrons by their respective atoms.
- The negative and positive ions so formed attain stable noble gas electronic configurations. The noble gases (with the exception of helium, which has a duplet of electrons) have a stable outer electronic configuration of eight (octet) electrons, $ns^2 np^6$.
What are the basis of Chemical Bond Formation ?
The facts given by W. Kossel are the basis of formation of chemical bonds.
- Atoms can also acquire noble gas configurations by sharing electrons with other atoms.
- Therefore, there are two main types of bonds:
- Ionic bond
- Covalent bond
Short Answer Conceptual Types Questions (SAT) on Octet Rule and Chemical Bonding
Q1. What is the octet rule in chemistry?
The octet rule states that atoms combine by either transferring or sharing electrons in order to achieve a stable configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell, similar to noble gases.
Q2. Who proposed the electronic theory of chemical bonding?
The theory was proposed in 1916 by W. Kossel and G. N. Lewis.
Q3. How do metals like Na, Mg, and Al achieve stability?
They achieve stability by losing their valence electrons to form cations with the noble gas configuration of neon ($1s^22s^22p^6$).
Q4. How do nonmetals like O and F achieve stability?
They gain electrons to form anions with noble gas configurations. For example, $O^{2-}$ and $F^-$ both have octets like neon.
Q5. What are the two main types of chemical bonds according to Kossel and Lewis?
The two main types are ionic bonds (transfer of electrons) and covalent bonds (sharing of electrons).
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) With Answers and Explanation on Octet Rule and Chemical Bonding
Q1. Which of the following best describes the octet rule?
(a) Atoms aim to have ten electrons in the outer shell
(b) Atoms aim to have eight electrons in the outer shell
(c) Atoms always lose electrons only
(d) Atoms always gain electrons only
Answer: (b) Atoms aim to have ten electrons in the outer shell
Q2. Sodium ($Na$) achieves stability by:
(a) Sharing electrons
(b) Gaining one electron
(c) Losing one electron
(d) Forming a covalent bond
Answer: (c) Losing one electron
Q3. Oxygen forms $O^{2-}$ ion because:
(a) It loses two electrons
(b) It shares two electrons
(c) It gains two electrons
(d) It remains inert
Answer: (c) It gains two electrons
Q4. Which configuration represents a stable octet?
(a) $1s^22s^22p^4$
(b) $1s^22s^22p^6$
(c) $1s^22s^22p^5$
(d) $1s^22s^22p^63s^1$
Answer: (b) $1s^22s^22p^6$
Q5. The two main types of bonds according to Lewis are:
(a) Ionic and Metallic
(b) Covalent and Metallic
(c) Ionic and Covalent
(d) Ionic and Coordinate
Answer: (c) Ionic and Covalent
Assertion Reason Type Questions With Answers and Explanation on Octet Rule and Chemical Bonding
Q1.
Assertion (A): Noble gases are chemically inert.
Reason (R): They have a complete octet (except helium, which has a duplet).
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, R is false.
(d) A is false, R is true.
Answer: (a)
Q2.
Assertion (A): Sodium forms $Na^+$ ion by losing one electron.
Reason (R): $Na^+$ has the same configuration as neon, which is a stable noble gas.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, R is false.
(d) A is false, R is true.
Answer: (a)
Q3.
Assertion (A): Oxygen forms $O^{2-}$ ion.
Reason (R): Oxygen achieves a neon-like configuration by losing two electrons.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, R is false.
(d) A is false, R is true.
Answer: (c) A is true, R is false.
Case Study on Octet Rule and Chemical Bonding
Read the following passage and answer the questions:
In 1916, W. Kossel and G. N. Lewis explained that atoms combine to achieve noble gas configurations. Metals like sodium, magnesium, and aluminium lose electrons to form cations, while nonmetals like oxygen and fluorine gain electrons to form anions. These ions attain the stable electronic configuration of neon ($1s^22s^22p^6$). The combination of positive and negative ions leads to ionic bond formation, while sharing of electrons leads to covalent bonding. This principle is summarized as the octet rule.
Questions:
Q1. Which scientist(s) introduced the electronic theory of bonding?
(a) Mendeleev and Moseley
(b) W. Kossel and G. N. Lewis
(c) Rutherford and Bohr
(d) Thomson and Millikan
Answer: (b)
Q2. Which ions are formed when sodium reacts with chlorine?
(a) $Na^+$ and $Cl^-$
(b) $Na^-$ and $Cl^+$
(c) $Na^{2+}$ and $Cl^-$
(d) $Na^+$ and $Cl^{2-}$
Answer: (a)
Q3. Oxygen achieves stability by:
(a) Losing 2 electrons
(b) Gaining 2 electrons
(c) Sharing electrons only with sodium
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Gaining 2 electrons
Q4. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred?
(a) Covalent bond
(b) Ionic bond
(c) Metallic bond
(d) Hydrogen bond
Answer: (b) Ionic bond
Q5. Which configuration corresponds to a noble gas octet?
(a) $1s^22s^22p^6$
(b) $1s^22s^22p^4$
(c) $1s^22s^22p^5$
(d) $1s^22s^22p^63s^1$
Answer: (a) $1s^22s^22p^6$