Anand Classes presents a detailed explanation of the Order of Energy Levels of Molecular Orbitals and Energy Level Diagram based on the Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT). Students will learn how the relative energy of σ (sigma) and π (pi) molecular orbitals changes for different diatomic molecules like B2, C2, N2, O2, and F2, and how this affects their bond order, stability, and magnetic properties. The topic is supported with clear energy level diagrams, solved examples, MCQs, Q&A, Assertion Reason, and Case Study questions for Class 11, Class 12, JEE, and NEET chemistry preparation. Click the print button to download study material and notes.
What are the Factors Affecting the Relative Energies of Molecular Orbitals?
The relative energies of molecular orbitals depend upon the following two factors:
- The energies of the atomic orbitals (AOs) combining to form molecular orbitals (MOs).
- The extent of overlapping between the atomic orbitals.
The greater the overlap, the more the bonding orbital is lowered and the antibonding orbital is raised in energy relative to AOs.
For example, the extent of overlapping in case of a σ-orbital is more than that in a π-orbital. Consequently, the energy of σ2pz is lower than the energy of bonding π2px or π2py molecular orbitals.
How are Molecular Orbitals Formed from 1s, 2s, and 2p Orbitals?
- The 1s AOs of two atoms form two MOs designated as σ1s and σ*1s.
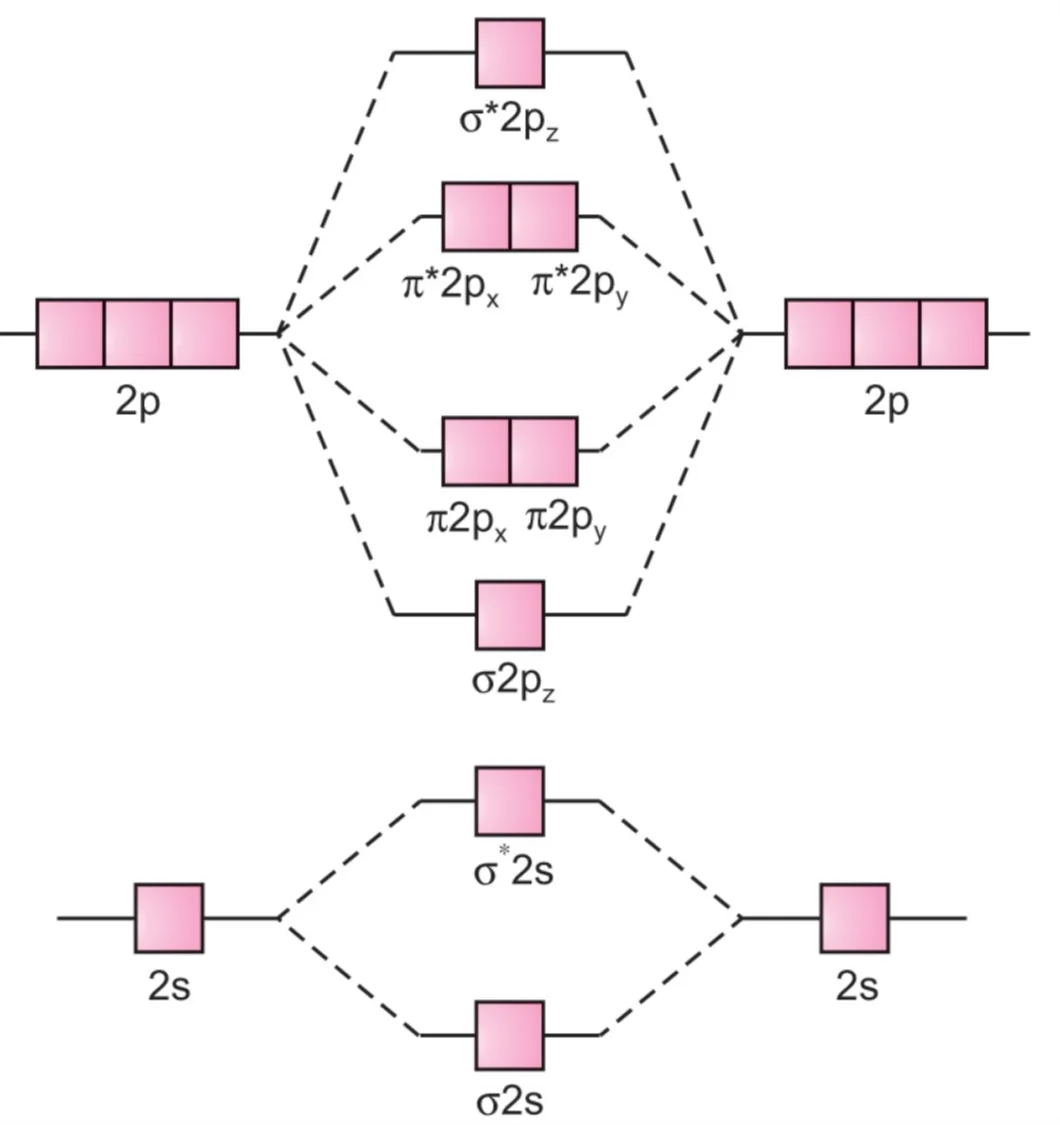
- The 2s and 2p orbitals (eight AOs on two atoms) form four bonding MOs and four antibonding MOs as:
Bonding MOs: σ2s, σ2pz, π2px, π2py
Antibonding MOs: σ*2s, σ*2pz, π*2px, π*2py
What is the General Order of Energy Levels of Molecular Orbitals?
The energy levels of these molecular orbitals have been determined experimentally by spectroscopic methods. The general order of increasing energy of MOs obtained by the combination of 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals of two atoms is as follows. For molecules from O2 onwards (O2, F2, Ne2), the order of energies of MOs is correct (σ2pz lower than π2px and π2py).:
$$\sigma 1s, \ \sigma^* 1s, \ \sigma 2s, \ \sigma^* 2s, \ \sigma 2p_z, \ \pi 2p_x = \pi 2p_y, \ \pi^* 2p_x = \pi^* 2p_y, \ \sigma^* 2p_z$$
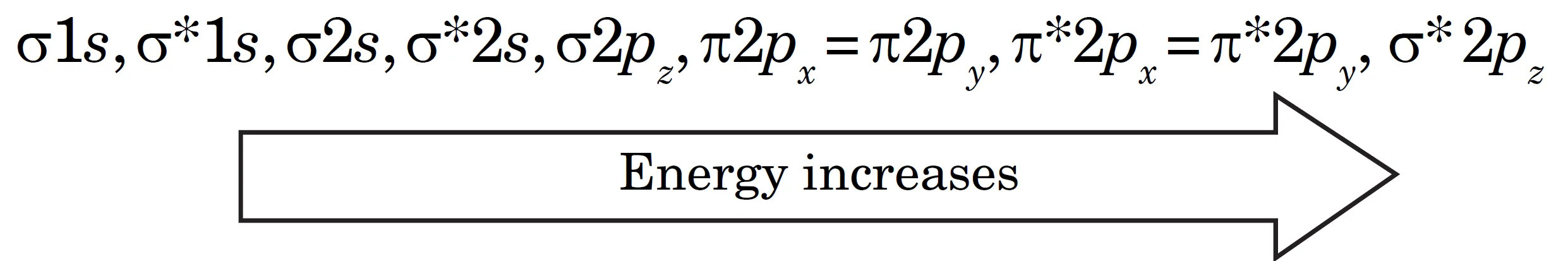
O2, F2, Ne2 molecules
Why Does the Energy Order Differ for Some Diatomic Molecules?
Experimental evidence has shown that the above sequence is not correct for all molecules.
- For homonuclear diatomic molecules of second-row elements (Li2, Be2, B2₂, C2, N2), the σ2pz MO is higher in energy than π2px and π2py MOs.
Energy order:
$$\sigma 1s, \ \sigma^* 1s, \ \sigma 2s, \ \sigma^* 2s, \ \pi 2p_x = \pi 2p_y, \ \sigma 2p_z, \ \pi^* 2p_x = \pi^* 2p_y, \ \sigma^* 2p_z$$
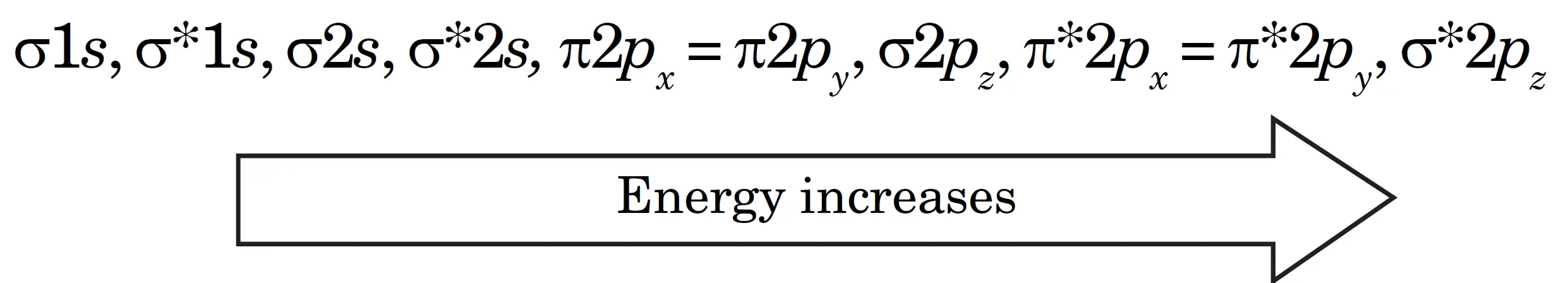
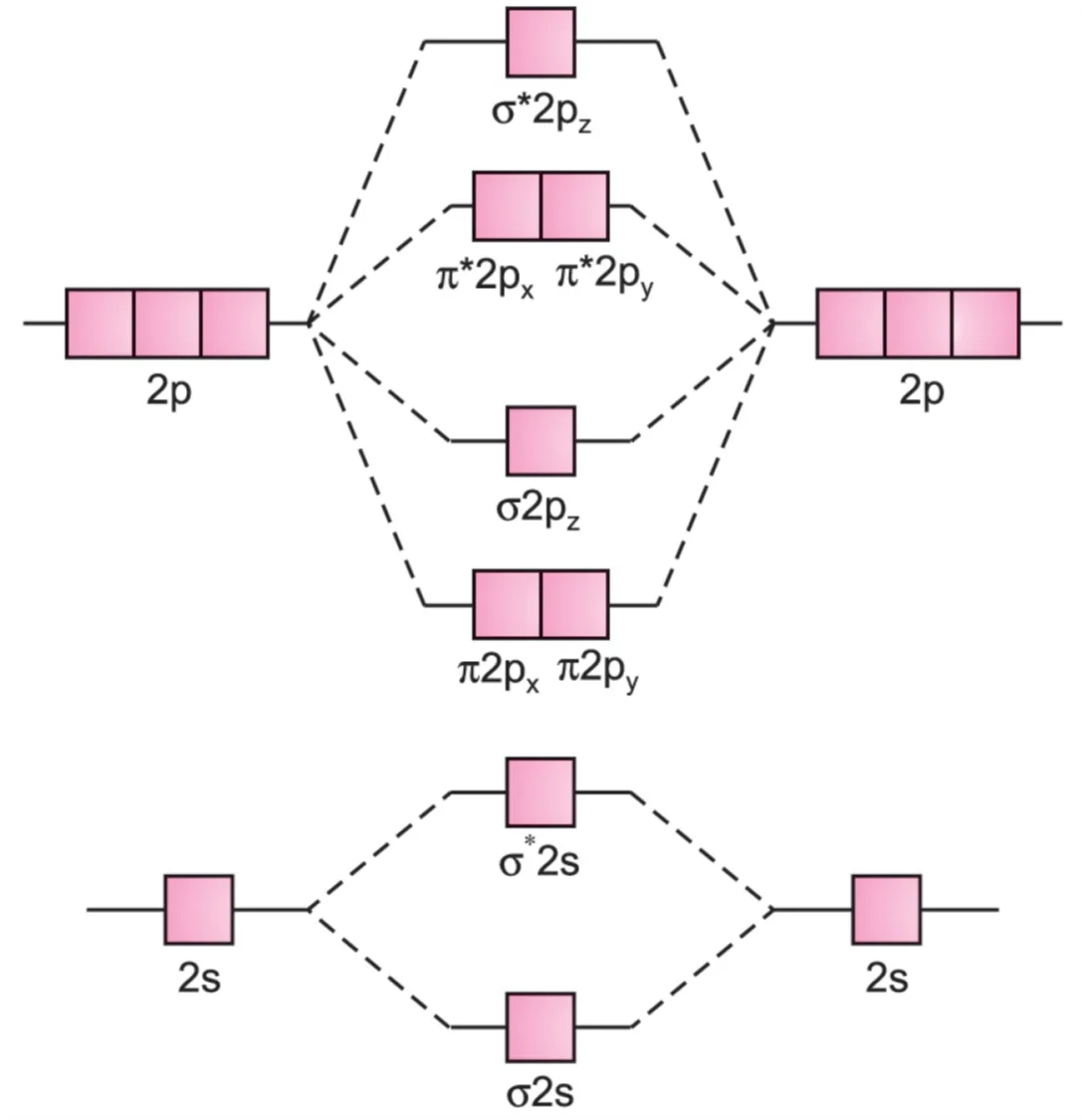
Li2, Be2, B2₂, C2, N2 molecules
Why Do Two Types of MO Energy Sequences Exist?
For diatomic molecules of the second period (Li2 to Ne2), there are two types of energy level diagrams:
- Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 → σ2pz MO is higher in energy than π2px and π2py.
- O2, F2, Ne2 → σ2pz MO is lower in energy than π2px and π2py.
Reason:
- For Li2 to N2: The difference in energies of 2s and 2pz orbitals is small, so they can interact.
- For O2 to Ne2: The difference in energies of 2s and 2pz orbitals is large, so no interaction occurs.
What are the Rules for Filling Molecular Orbitals?
The following rules are followed to write molecular electronic configurations:
- Aufbau Principle: The molecular orbital having the lowest energy is filled first.
- Pauli’s Exclusion Principle: Each molecular orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
- Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity: If two or more MOs of the same energy are available, one electron enters each orbital singly before pairing occurs.
📘 Practice Questions on Energy Level Diagram of Molecular Orbitals
Short Answer Conceptual Types (SAT)
Q1. On what factors do the relative energies of molecular orbitals depend?
Answer:
They depend on:
- Energies of atomic orbitals (AOs) combining to form MOs.
- Extent of overlapping between AOs. Greater overlap → bonding orbital lowered and antibonding orbital raised in energy.
Q2. Why is the energy of σ2pz orbital lower than that of π2px and π2py in O₂ and F₂?
Answer:
In O₂ and F₂, the difference between 2s and 2pz AOs is large, so they do not interact. As a result, σ2pz is lower in energy than π2px and π2py.
Q3. Why do Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂ show a different MO energy order than O₂ and F₂?
Answer:
For Li₂ to N₂, the difference in energies of 2s and 2pz orbitals is small, hence 2s–2pz mixing (interaction) occurs, pushing σ2pz higher than π2px/π2py.
Q4. State the three rules for filling electrons in molecular orbitals.
Answer:
- Aufbau principle – fill orbitals of lowest energy first.
- Pauli’s exclusion principle – max two electrons per orbital with opposite spins.
- Hund’s rule – orbitals of equal energy are singly occupied before pairing.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Which of the following is correct order of molecular orbitals for O2?
(a) σ1s < σ1s < σ2s < σ2s < σ2pz < π2px = π2py < π2px = π2py < σ2pz
(b) σ1s < σ1s < σ2s < σ2s < π2px = π2py < σ2pz < π2px = π2py < σ2pz
(c) σ1s < σ1s < σ2s < σ2s < π2px = π2py < π2px = π2py < σ2pz < σ*2pz
(d) None of these
Answer: (a)
Explanation: For O₂ onwards, σ2pz lies below π2px and π2py.
Q2. The difference in energy sequences of MOs between N2 and O2 is mainly due to:
(a) Difference in atomic size
(b) 2s–2pz mixing (interaction)
(c) Nuclear charge difference
(d) Electronegativity difference
Answer: (b)
Explanation: For lighter molecules (Li2–N2), 2s and 2pz orbitals are close in energy → mixing occurs.
Q3. In σ2pz orbital, electron density lies:
(a) Above and below internuclear axis
(b) On the internuclear axis
(c) Away from nuclei
(d) Symmetrically distributed outside bond axis
Answer: (b)
Explanation: By definition, σ-orbitals have electron density along internuclear axis.
Assertion-Reason Type Questions
Q1.
Assertion (A): In B2 molecule, the σ2pz orbital has higher energy than π2px and π2py orbitals.
Reason (R): In B2, 2s–2pz mixing is significant.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, R is false.
(d) A is false, R is true.
Answer: (a)
Explanation: In lighter diatomics (up to N2), σ2pz is above π2px/π2py due to 2s–2pz mixing.
Q2.
Assertion (A): In O2 molecule, σ2pz orbital is lower in energy than π2px and π2py.
Reason (R): In O2, energy difference between 2s and 2pz orbitals is large, so they cannot mix.
Options: (a) True, correct explanation (b) True, not explanation (c) False, True (d) False, False
Answer: (a)
Explanation: Absence of 2s–2pz mixing in O2 leads to σ2pz < π2px/π2py.
Case Study
Passage:
The molecular orbital (MO) theory explains bonding in diatomic molecules. For Li2, Be2, B2, C2, and N2, the order of MOs is:
$$\sigma 1s < \sigma^1s < \sigma 2s < \sigma^2s < \pi 2p_x = \pi 2p_y < \sigma 2p_z < \pi^ 2p_x = \pi^ 2p_y < \sigma^* 2p_z$$
For O2, F2, and Ne2, the order is:
$$\sigma 1s < \sigma^1s < \sigma 2s < \sigma^2s < \sigma 2p_z < \pi 2p_x = \pi 2p_y < \pi^ 2p_x = \pi^ 2p_y < \sigma^* 2p_z$$
This difference is due to 2s–2pz mixing.
Questions:
- Which orbital is higher in energy in N2, σ2pz or π2px?
- Which orbital is lower in energy in O2, σ2pz or π2px?
- Why does mixing not occur in O2 and F2?
- What rules govern electron filling in MOs?
Answers:
- In N2, σ2pz is higher in energy than π2px.
- In O2, σ2pz is lower in energy than π2px.
- Mixing does not occur because energy difference between 2s and 2pz AOs is large.
- Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle, Hund’s rule govern electron filling.