Anand Classes offers comprehensive NCERT Exemplar Solutions for questions 24 to 30 (Short Answer Type Questions) from the chapter Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties for Class 11 Chemistry. These solutions are carefully crafted to help students grasp important periodic trends, properties of elements, and classification techniques with clear explanations, examples, and illustrations for better understanding and effective exam preparation. Click the print button to download study material and notes.
Question 24
Explain why the electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than that of chlorine?
Answer:
The electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than that of chlorine because:
- In fluorine, the added electron enters the small n = 2 quantum level, where it suffers strong electron-electron repulsions.
- In chlorine, the added electron enters the larger n = 3 quantum level, where repulsions are much less.
Thus, Cl has more negative electron gain enthalpy than F.
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{\Delta_{eg}H_{Cl} < 0 \; \text{(more negative) than} \; \Delta_{eg}H_{F}} $$
Question 25
All transition elements are d-block elements, but all d-block elements are not transition elements. Explain.
Answer:
- Elements in which the last electron enters a d-orbital are called d-block elements.
- Transition elements have the general configuration: $(n-1)d^{1-10} ns^{0-2}$.
- Examples: Zn, Cd, Hg have configuration $(n-1)d^{10} ns^2$. Their d-orbitals are completely filled in both ground state and common oxidation states.
- Therefore, Zn, Cd, Hg do not show typical transition properties.
Hence:
- All transition elements are d-block elements,
- But not all d-block elements are transition elements.
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{\text{Zn, Cd, Hg are exceptions → not transition elements}} $$
Question 26
Identify the group and valency of the element having atomic number 119. Also predict the outermost electronic configuration and write the general formula of its oxide.
Answer:
- Current periodic table accommodates up to 118 elements. The next element (Z = 119) will have its last electron in the 8s orbital.
- Configuration: $[Og] \, 8s^1$.
- Since it has one valence electron, valency = 1.
- It will belong to Group 1 (alkali metals).
- General oxide formula: $M_2O$.
Final Answer:
Group 1, Valency = 1, Configuration = 8s1, Oxide = M2O
Question 27
Ionisation enthalpies of elements of the second period are given:
520, 899, 801, 1086, 1402, 1314, 1681, 2080 (kcal mol$^{-1}$). Match with correct elements and complete the graph.
Answer:
- As we move left to right in a period, ionisation enthalpy generally increases due to increasing nuclear charge and decreasing size.
- Exceptions:
- Be > B: Be has a stable fully-filled 2s orbital, so removing an electron requires more energy. B loses from 2p, easier.
- N > O: N has a stable half-filled 2p^3 configuration. O has paired electrons in one 2p orbital, so repulsion lowers ionisation enthalpy.
Thus the sequence is:
- Li (520), Be (899), B (801), C (1086), N (1402), O (1314), F (1681), Ne (2080).
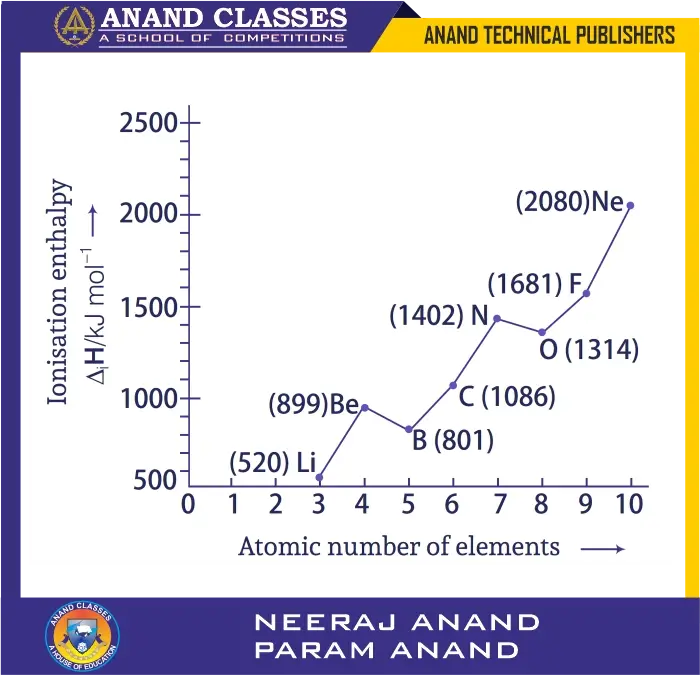
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{\text{Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne with their respective values}} $$
Question 28
Among the elements B, Al, C, and Si:
(a) Which element has the highest first ionisation enthalpy?
(b) Which element has the most metallic character?
Answer:
- (a) Ionisation enthalpy increases left to right across a period and decreases down a group.
→ Carbon has the highest ionisation enthalpy. - (b) Metallic character decreases across a period but increases down the group.
→ Aluminium has the most metallic character.
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{\text{Highest I.E. → C, Most Metallic → Al}} $$
Question 29
Write four characteristic properties of p-block elements.
Answer:
(a) Both metals and non-metals present, but non-metals are more numerous.
- Metallic character increases down a group.
- Non-metallic character increases left to right in a period.
(b) Ionisation enthalpies are relatively high compared to s-block.
(c) They mostly form covalent compounds.
(d) Many show variable oxidation states.
- Oxidising character increases left to right.
- Reducing character increases top to bottom.
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{\text{Variable properties, covalent nature, high I.E., metals + non-metals}} $$
Question 30
Choose the correct order of atomic radii of fluorine and neon (in pm):
(a) 72, 160
(b) 160, 160
(c) 72, 72
(d) 160, 72
Answer: Correct Option (a)
- Atomic radius of fluorine is expressed as covalent radius.
- Atomic radius of neon is usually expressed as van der Waals radius, which is always larger than covalent radius.
- Therefore, $r_F < r_{Ne}$.
Numerical values:
$F = 72 \, pm, \; Ne = 160 \, pm$
Final Answer:
$$ \boxed{F = 72 \, pm, \; Ne = 160 \, pm} $$
📚 Buy Study Material & Join Our Coaching
For premium study materials specially designed for JEE, NEET, NDA, and CBSE/ICSE Classes, visit our official study material portal:
👉 https://publishers.anandclasses.co.in/
For NDA Study Material, Click Here
For SSC Study Material, Click Here
To enroll in our offline or online coaching programs, visit our coaching center website:
👉 https://anandclasses.co.in/
📞 Call us directly at: +91-94631-38669
💬 WhatsApp Us Instantly
Need quick assistance or want to inquire about classes and materials?
📲 Click below to chat instantly on WhatsApp:
👉 Chat on WhatsApp
🎥 Watch Video Lectures
Get access to high-quality video lessons, concept explainers, and revision tips by subscribing to our official YouTube channel:
👉 Neeraj Anand Classes – YouTube Channel


