Trigonometry is one of the major topics in Maths subject. Trigonometry deals with the measurement of angles and sides of a triangle. Usually, trigonometry is considered for the right-angled triangle. Also, its functions are used to find out the length of the arc of a circle, which forms a section in the circle with a radius and its center point.
If we break the word trigonometry, ‘Tri’ is a Greek word which means ‘Three’, ‘Gon’ means ‘length’, and ‘metry’ means ‘measurement’. So basically, trigonometry is a study of triangles, which has angles and lengths on its side. Trigonometry basics consist of sine, cosine and tangent functions. Trigonometry for class 11 contains trigonometric functions, identities to solve complex problems more simply.
Table of Contents
Trigonometry Formulas
Here, you will learn trigonometry formulas for class 11 and trigonometric functions of Sum and Difference of two angles and trigonometric equations.
Starting with the basics of Trigonometry formulas, for a right-angled triangle ABC perpendicular at B, having an angle θ, opposite to perpendicular (AB), we can define trigonometric ratios as;
Sin θ = P/H
Cos θ = B/H
Tan θ = P/B
Cot θ = B/P
Sec θ = H/B
Cosec θ = H/P
Where,
P = Perpendicular
B = Base
H = Hypotenuse
Trigonometry Functions
Trigonometry functions are measured in terms of radian for a circle drawn in the XY plane. Radian is nothing but the measure of an angle, just like a degree. The difference between the degree and radian is;
Degree: If rotation from the initial side to the terminal side is (1/360)th of revolution, then the angle is said to measure 1 degree.
1 degree=60minutes
1 minute=60 second
Radian: If an angle is subtended at the center by an arc of length ‘l, the angle is measured as radian. Suppose θ is the angle formed at the center, then
θ = Length of the arc/radius of the circle.
θ = l/r
Relation between Degree and Radian:
2π radian = 360°
Or
π radian = 180°
Where π = 22/7
Learn more about the relation between degree and radian here.
Table for Degree and Radian relation
| Degree | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| Radian | π/6 | π/4 | π/3 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 2π |
Earlier we have discussed of trigonometric ratios for a degree, here we will write the table in terms of radians.
Trigonometry Table
| Angle | 0 | π/6 | π/4 | π/3 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 2π |
| sin θ | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 |
| cos θ | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| tan θ | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | undefined | 0 | undefined | 0 |
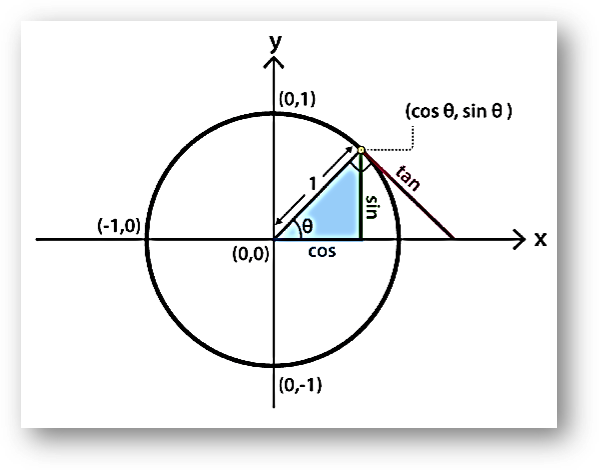
Sign of Trigonometric Functions
sin(-θ) = -sin θ
cos(-θ) = cos θ
tan(-θ) = -tan θ
cot(-θ) = -cot θ
sec(-θ) = sec θ
cosec(-θ) = -cosec θ
Click here to know more about the sign of trigonometric functions.
Also, go through the table given below to understand the behaviour of trigonometric functions with respect to their values in different quadrants.
| Quadrant I | Quadrant II | Quadrant III | Quadrant IV | |
| sin | Increases from 0 to 1 | Decreases from 1 to 0 | Decreases from o to -1 | Increases from -1 to 0 |
| cos | Decreases from 1 to 0 | Decreases from o to -1 | Increases from -1 to 0 | Increases from 0 to 1 |
| tan | Increases from 0 to ∞ | Increases from -∞ to 0 | Increases from 0 to ∞ | Increases from -∞ to 0 |
| cosec | Decreases from ∞ to 1 | Increases from 1 to ∞ | Increases from -∞ to 1 | Decreases from -1 to ∞ |
| sec | Increases from 1 to ∞ | Increases from -∞ to 1 | Decreases from -1 to ∞ | Decreases from ∞ to 1 |
| cot | Decreases from ∞ to 0 | Decreases from 0 to -∞ | Decreases from ∞ to 0 | Decreases from 0 to -∞ |
This behaviour can be observed from the trigonometry graphs.
Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Product of two angles
(I)
sin (x+y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y
sin (x-y) = sin x cos y – cos x sin y
cos (x+y) = cos x cos y – sin x sin y
cos (x-y) = cos x cos y + sin x sin y
sin (π/2 – x) = cos x
cos (π/2 – x) = sin x
(II)
tan (x+y) = (tan x + tan y) /(1−tan x tan y)
tan (x-y) = (tan x − tan y)/(1 + tan x tan y)
cot (x+y) = (cot x cot y −1)/(cot y + cot x)
cot(x-y) = (cot x cot y + 1)/( cot y − cot x)
(III)
cos 2x = cos2 x-sin2 x = 2cos2 x-1 = 1-2sin2 x = (1-tan2 x)/(1+tan2 x)
sin 2x = 2sin x cos x= 2tan x/(1+ tan2 x)
tan 2x = 2 tan x/(1-tan2 x)
(IV)
sin 3x = 3 sin x – 4 sin3 x
cos 3x = 4 cos3 x – 3 cos x
tan 3x = [3tan x-tan3 x]/[1-3 tan2 x]
(V)
\(\begin{array}{l}cos\ x+ cos\ y=2\ cos{(\frac{x+y}{2})}\ cos{(\frac{x-y}{2})}\\ cos\ x – cos\ y = -2\ sin{(\frac{x+y}{2})}\ sin{(\frac{x-y}{2})}\\ sin\ x + sin\ y = 2\ sin{(\frac{x+y}{2})}\ cos{(\frac{x-y}{2})}\\ sin\ x – sin\ y = 2\ cos{(\frac{x+y}{2})}\ sin{(\frac{x-y}{2})}\end{array} \)
(VI)
2 cos x cos y = cos (x+y) + cos (x-y)
2 sin x sin y = cos (x-y) – cos (x+y)
2 sin x cos y= sin (x+y) + sin (x-y)
2 cos x sin y = sin (x+y) – sin (x-y)
To solve the trigonometric questions for class 11, all these functions and formulas are used accordingly. By practising those questions, you can memorize the formulas as well.
Solved Examples
Example 1:
Prove that sin(x+y)/ sin(x−y) = (tan x + tan y)/(tan x–tan y)
Solution:
We have
LHS = sin(x+y)/sin(x−y)
= (sin x cos y + cos x sin y)/(sin x cos y − cos x sin y)
Dividing numerator and denominator by cos x cos y, we get
= (tan x + tan y)/(tan x–tan y) ———–Proved.
Example 2:
Find the value of cos (31π/3).
Solution:
We know that the value of cos x repeats after the interval 2π.
Thus, cos (31π/3) = cos (10π + π/3)
= cos π/3 = 1/2
- Trigonometric Functions and Their Properties
- Sum and Product of Two Angles Formulas
- Relation Between Degree and Radian in Trigonometry
- Trigonometry Table for Class 11 Math
- Trigonometric Formulas for JEE
- Trigonometric Functions PDF Download
- Sum and Product of Angles Trigonometry Examples
- Degree to Radian and Radian to Degree Conversion
- Trigonometry Table for Sin, Cos, Tan Values
- Important Trigonometric Identities for JEE


