Anand Classes offers detailed and reliable Sets NCERT Solutions Exercise 1.5 Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 to help students strengthen their understanding of key concepts in set theory. These solutions are prepared according to the latest NCERT and CBSE syllabus, providing step-by-step explanations for each question to ensure complete conceptual clarity. Perfect for Class 11 students revising for exams, these solutions make learning smooth, systematic, and exam-oriented. Click the print button to download study material and notes.
NCERT Question 1. Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {2, 4, 6, 8} and C = {3, 4, 5, 6}. Find:
(i) A’ $\quad $ (ii) B′ $\quad $ (iii) (A ∪ C)′ $\quad $ (iv) (A ∪ B)′$\quad $
(v) (A′)′ $\quad $ (vi) (B – C)′.
Solution :
(i)
A′ = U – A = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 1, 2, 3, 4 } = { 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }
(ii)
B′ = U – B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 2, 4, 6, 8 } = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 }
(iii)
A ∪ C = { 1, 2, 3, 4 } ∪ { 3, 4, 5, 6 } = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }
(A ∪ C)′= U – (A ∪ C) = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 } = { 7, 8, 9 }
(iv)
A ∪ B = { 1, 2, 3, 4 } ∪ { 2, 4, 6, 8 } = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 }
(A ∪ B)′= U – (A ∪ B) = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 } = { 5, 7, 9 }
(v)
A′ = U – A = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 1, 2, 3, 4 } = { 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }
(A′)′ = U – A′ = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } = { 1, 2, 3, 4 } = A
(vi)
B – C = { 2, 4, 6, 8 } – { 3, 4, 5, 6 } = { 2, 8 }
(B – C)′= U – (B – C) = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } – { 2, 8 } = { 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9 }.
NCERT Question 2. If U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h}, find the complements of the following sets :
(i) A = { a, b, c}
(ii) B = { d, e, f, g }
(iii) C = { a, c, e, g}
(iv) D = { f, g, h, a }
Solution :
(i) A = { a, b, c}
Complement of set A = A
A’ = U – A
A’ = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} – {a, b, c}
A’ = {d, e, f, g, h}
(ii)
(ii) B = { d, e, f, g }
Complement of set B = B’
B’ = U – B
B’ = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} – {d, e, f, g}
B’ = {a, b, c, h}
(iii) C = {a, c, e, g}
Complement of set C = C’
C’ = U – C
C’ = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} – {a, c, e, g}
C’ = {b, d, f, h}
(iv) D = {f, g, h, a}
Complement of set D = D’
D’ = U – D
D’ = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} – {f, g, h, a}
D’ = {b, c, d, e}
NCERT Question 3. Taking the set of natural numbers as the universal set, write down the complements of the following sets:
(a) {x : x is an even natural number}
(b) {x : x is an odd natural number}
(c) {x : x is a positive multiple of 3}
(d) {x : x is a prime number}
(e) {x : x is a natural number divisible by 3 and 5}
(f) {x : x is a perfect square}
(g) {x : x is a perfect cube}
(h) {x : x + 5 = 8}
(i) {x : 2x + 5 = 9}
(j) {x : x ≥ 7}
(k) {x : x ∈ N and 2x + 1 > 10}
Solution : Let
U = N: set of natural numbers
(a) {x : x is an even natural number}
=> {x : x is an odd natural number}
(b) {x : x is an odd natural number}
=>{x : x is an even natural number}
(c) {x : x is a positive multiple of 3}
=>{x : x ∈ N and x is not a multiple of 3}
(d) {x : x is a prime number}
=> {x : x is a positive composite number and x = 1}
Def: Composite number: A natural number > 1 is said to be composite if it is not prime, i.e., if it has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. For example, 4, 6, 8, 9, … are composite.
Note. In fact N is the union of (set of primes, set of composites and {1})
(e) {x : x is a natural number divisible by 3 and 5}
=> {x : x is a natural number that is not divisible by 3 or 5}
(f) {x : x is a perfect square}
=> {x : x∈N and x is not perfect square}
(g) {x : x is a perfect cube}
=> {x : x ∈ N and x is not perfect cube}
(h) {x : x + 5 = 8}
=> {x : x ∈ N and x ≠ 3}
(i) {x : 2x + 5 = 9}
=> {x : x ∈ N and x ≠ 2}
(j) {x : x ≥ 7}
=> {x : x∈N and x < 7}
(k) {x : x ∈ N and 2x + 1 > 10}
=> {x : x∈N and x ≤ 9/2} = {1, 2, 3, 4}
Question 4. If U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, A = {2, 4, 6, 8} and B = { 2, 3, 5, 7}. Verify that
(a) (A ∪ B)’= A’ ∩ B’
(b) (A ∩ B)′ = A′ ∪ B′
Solution:
(a) (A ∪ B)’= A’ ∩ B’
=> (A ∪ B)’= U – (A∪B)
=> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
=> (A∪B)’ = {1, 9}
A’ ∩ B’ = (U – A) ∩ (U – B)
=> {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} ∩ {1, 4, 6, 8, 9}
=> A’ ∩ B’ = {1, 9}
Hence, Verified!!! (A∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
(b) (A ∩ B)′ = A′ ∪ B′
=> (A ∩ B)’ = U – (A ∩ B)
=> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {2}
=> (A ∩ B)′ = {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
A’ ∪ B’= (U – A) ∪ (U – B)
=> {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} ∪ {1, 4, 6, 8, 9}
=> A′ ∪ B′ = {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
Hence, Verified!!! (A ∩ B)′ = A′ ∪ B′
NCERT Question 5. Draw appropriate Venn diagram for each of the following:
(i) (A ∪ B)′ (ii) A′ ∩ B′ (iii) (A ∩ B)′ (iv) A′ ∪ B′.
(a) (A ∪ B)′ =
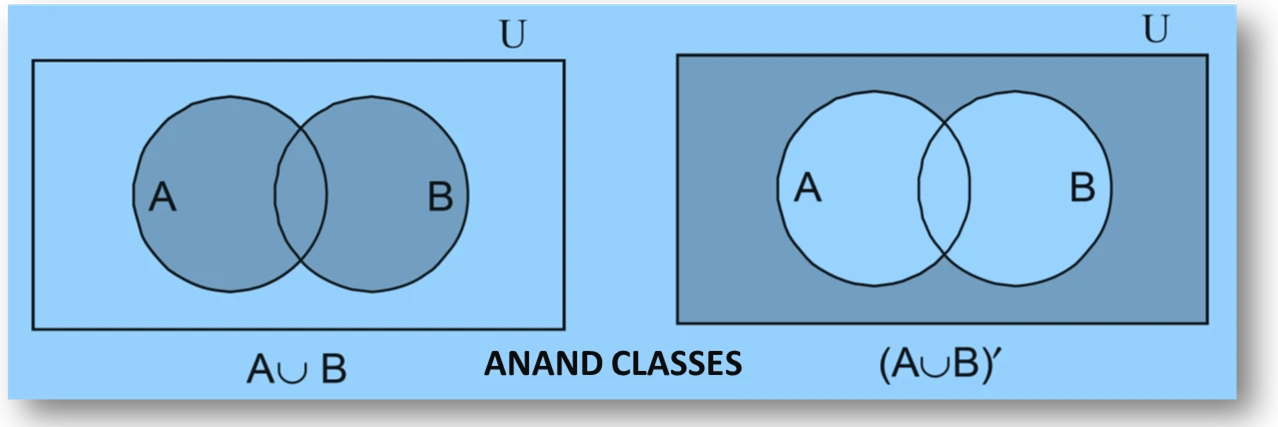
(b) A’ ∩ B’ =
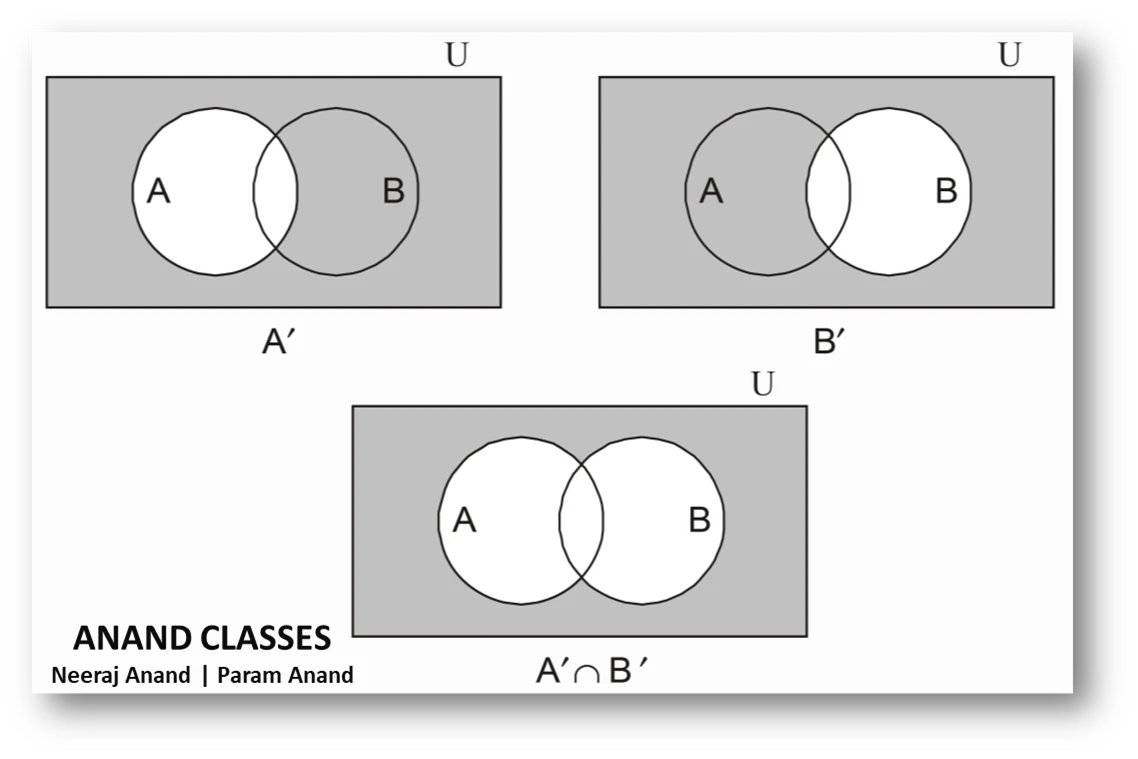
(c) (A ∩ B)′ =
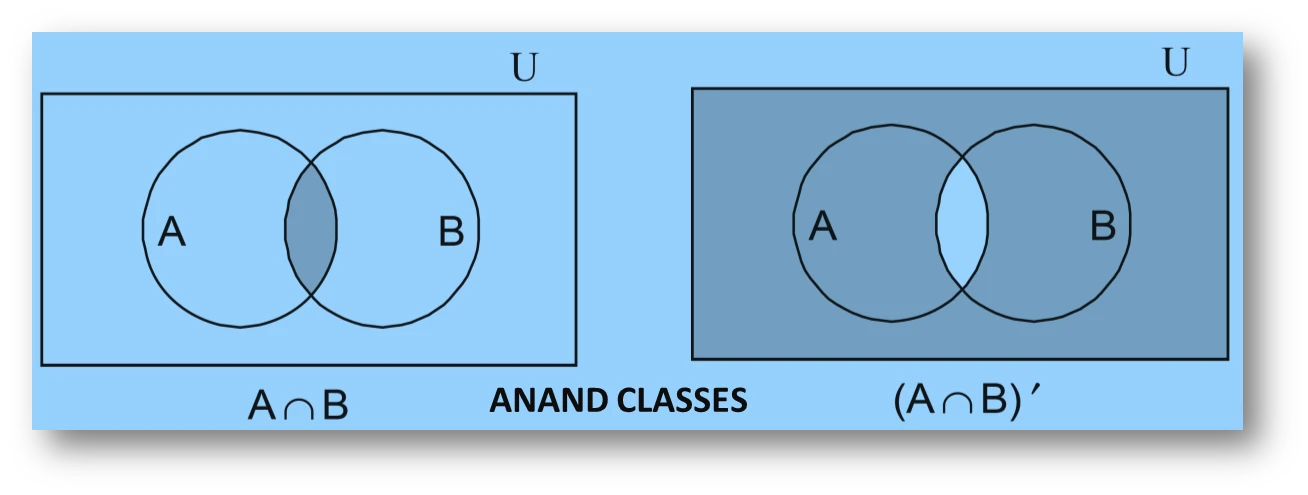
(d) A′ ∪ B′ =
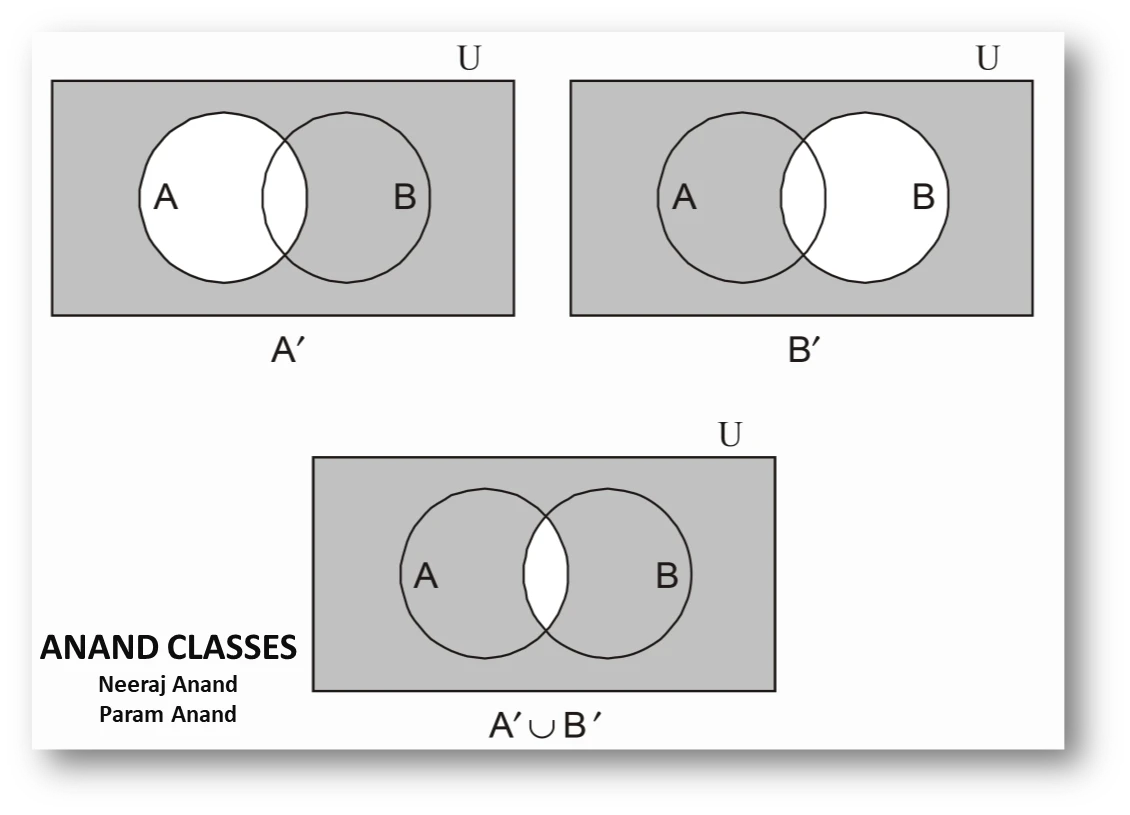
NCERT Question 6. Let U be the set of all triangles in a plane. If A is the set of all triangles with atleast one angle different from 60°, what is A′?
Solution:
U = set of all triangles in plane
A′ = U – A
A = set of all triangles with at least one angle different from 60°
A’ = set of all triangles with no angle different from 60° i.e, set of all triangles with all angles 60°
A’ is the set of all equilateral triangle.
NCERT Question 7. Fill in the blanks to make each of the following a true statement :
(a) A ∪ A′ = …
(b) φ′ ∩ A = …
(c) A ∩ A′ = …
(d) U′ ∩ A = …
Solution:
(a) A ∪ A′ = U
(b) ∅′ ∩ A = A
(c) A ∩ A′ = ∅
(d) U′ ∩ A = ∅


