Anand Classes provides detailed NCERT Solutions for Exercise 8.1 from Chapter 8 Applications of Integrals for Class 12 Mathematics, helping students understand the concept of finding the area under curves with clear explanations and step-by-step solutions. These notes follow the latest NCERT and CBSE syllabus and are ideal for revision, competitive exam preparation, and building strong conceptual understanding. Click the print button to download study material and notes.
NCERT Question.1 : Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse
$$ \frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$
Solution :
Equation of ellipse is :
$$ \frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$

$$ \frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$
Use area as area under curve (quarter-area method). Solve for the upper half of the ellipse:
$$y=b\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}}\qquad a=4, b=3$$
Area of the whole ellipse = four times the area in the first quadrant (say OAB):
$$
\text{Area}=4\int_{0}^{a} y\;dx
=4\int_{0}^{4} 3\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{16}}\;dx
=12\int_{0}^{4}\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{16}}\;dx.
$$
Use the substitution $x=a\sin\theta=4\sin\theta$, so $dx=4\cos\theta\;d\theta$. When $x=0\Rightarrow\theta=0$, and $x=4\Rightarrow\theta=\dfrac{\pi}{2}$. Then
$$\text{Area}
=12\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\sqrt{1-\sin^{2}\theta}(4\cos\theta)\;d\theta =12\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}( \cos\theta)(4\cos\theta)\;d\theta$$
$$\text{Area}=48\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\cos^{2}\theta\;d\theta
=48\cdot\frac{1}{2}\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}(1+\cos 2\theta)\;d\theta$$
$$\text{Area}=24\left[\theta+\tfrac{1}{2}\sin 2\theta\right]_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}
=24\left(\frac{\pi}{2}+0\right)
=12\pi.
$$
$$
\boxed{\;\text{Area}=12\pi\;\text{square units}\;}
$$
Download notes by Anand Classes — perfect for JEE and CBSE practice and clear step-by-step integral methods.
NCERT Question.2 : Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse
$$\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$
Solution
The given equation of ellipse is
$$\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$
which has
$$a=2 \quad\text{and}\quad b=3.$$
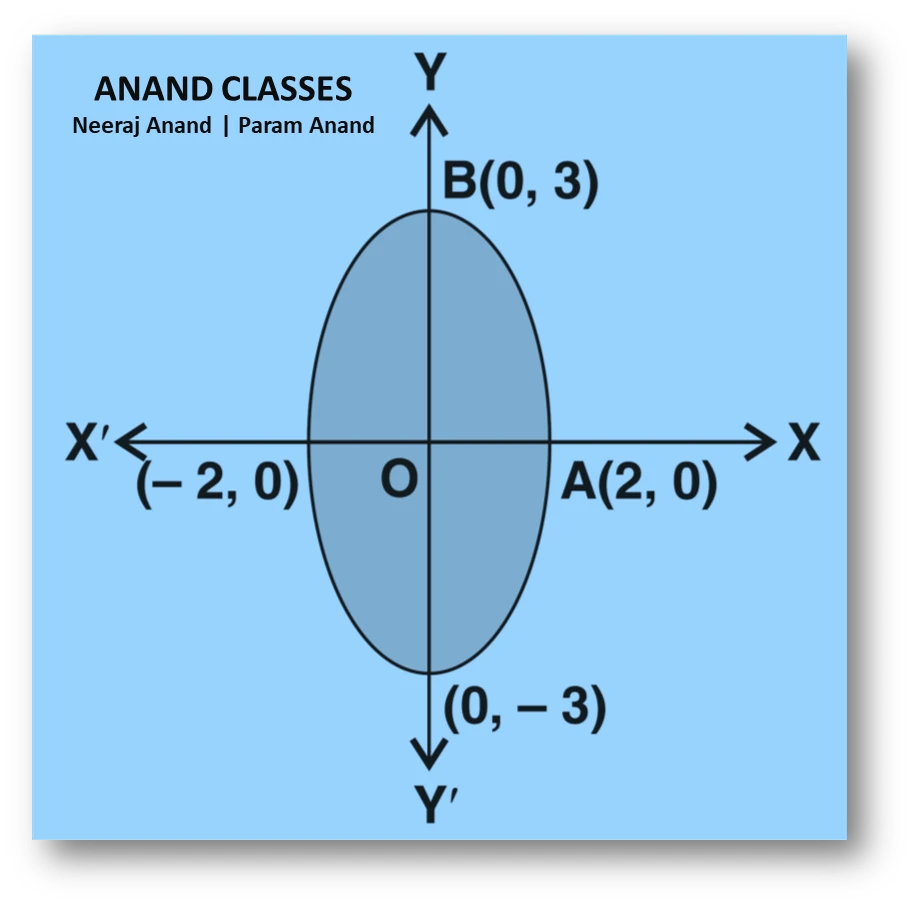
$$\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$$
The upper half of the ellipse can be written as
$$y=3\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}}.$$
The total area is four times the area in the first quadrant:
$$A=4\int_{0}^{2}3\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}}\;dx.$$
So,
$$A=12\int_{0}^{2}\sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}}\;dx.$$
Substitute
$$x=2\sin\theta \quad\Rightarrow\quad dx=2\cos\theta\;d\theta.$$
When $x=0\Rightarrow\theta=0$
When $x=2\Rightarrow\theta=\frac{\pi}{2}$
Thus,
$$A=12\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\sqrt{1-\sin^{2}\theta}\;(2\cos\theta)\;d\theta$$
$$A=24\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\cos^{2}\theta\;d\theta.$$
Use
$$\cos^{2}\theta=\frac{1+\cos 2\theta}{2}.$$
So,
$$A=24\int_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1+\cos 2\theta}{2}\;d\theta$$
$$A=12\left[\theta+\frac{1}{2}\sin 2\theta\right]_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}$$
$$A=12\cdot\frac{\pi}{2}=6\pi.$$
Final Result
$$\boxed{6\pi\;\text{square units}}$$
Score higher with expertly crafted solutions and step-by-step notes by Anand Classes, ideal for CBSE and JEE preparation.
NCERT Question.3 : Area lying in the first quadrant and bounded by the circle
$$ x^{2}+y^{2}=4 $$
and the lines $(x=0)$ and $(x=2)$ is:
(A) $\pi $
(B) $ \frac{\pi}{3} $
(C) $ \frac{\pi}{2} $
(D) $\frac{7\pi}{4} $
Solution :
The equation of circle is
$$ x^{2}+y^{2}=4. $$
Thus the radius is $2$. In the first quadrant,
$$ y=\sqrt{4-x^{2}}. $$
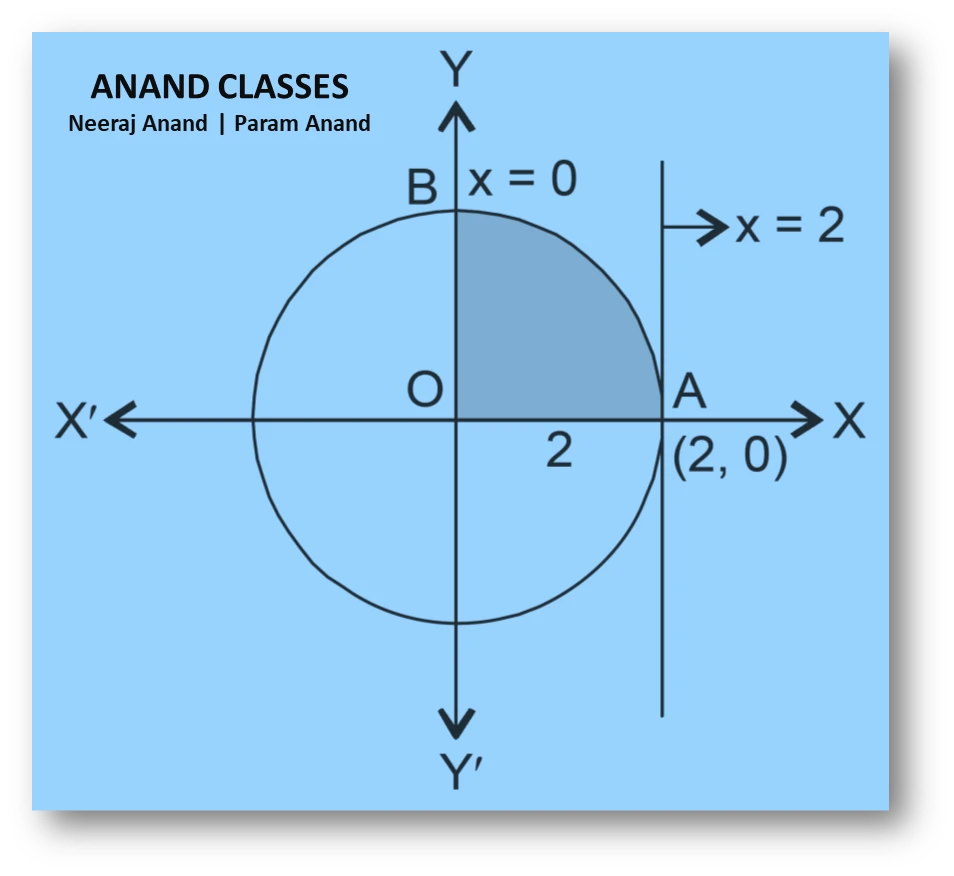
$$ x^{2}+y^{2}=4 $$
and the lines $(x=0)$ and $(x=2)$ is:
Required area:
$$ A=\int_{0}^{2}\sqrt{4-x^{2}}\;dx $$
Use the standard integral:
$$ \int \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}\;dx = \frac{x}{2}\sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2}\sin^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{a}\right)+C $$
Here $a=2$, so
$$
A=\left[\frac{x}{2}\sqrt{4-x^{2}}+2\sin^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)\right]_{0}^{2}.
$$
At $x=2$:
$$
\frac{2}{2}\cdot 0 + 2\sin^{-1}(1)= 2\cdot \frac{\pi}{2} = \pi.
$$
At $x=0$:
$$
0+2\sin^{-1}(0)=0.
$$
Thus,
$$ A=\pi-0=\pi. $$
Correct Answer: (A) $( \pi )$
NCERT Question.4 : Area of the region bounded by the curve
$ y^{2}=4x, $ the y-axis and the line $ y=3 $ is:
(A) $2$
(B) $ \frac{9}{4} $
(C) $ \frac{9}{3} $
(D) $ \frac{9}{2} $
Solution
The curve is the rightward parabola
$$ y^{2}=4x. $$
From it,
$$ x=\frac{y^{2}}{4}. $$
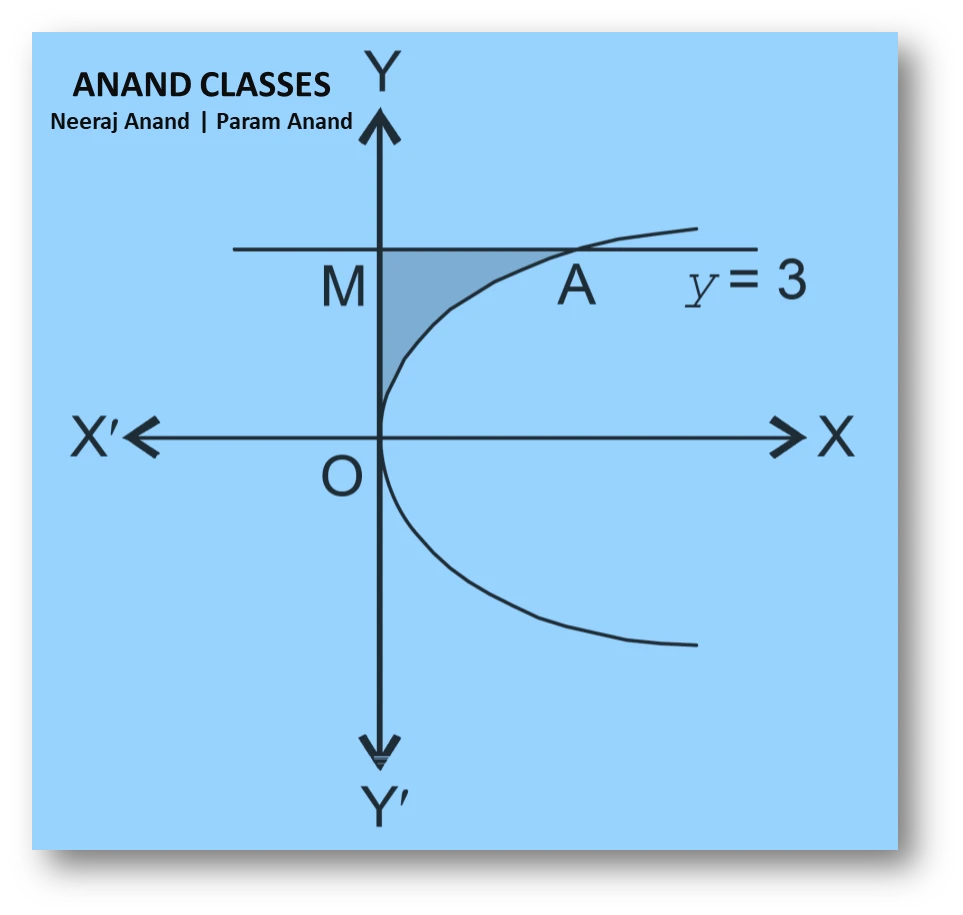
$ y^{2}=4x, $ the y-axis and the line $ y=3 $ is:
Required area (bounded by the parabola, y-axis, and $(y=3)$ is
$$ A=\int_{0}^{3} x\;dy. $$
Substitute $ x=\dfrac{y^{2}}{4} $:
$$
A=\int_{0}^{3} \frac{y^{2}}{4}\;dy.
$$
Compute:
$$
A=\frac{1}{4}\int_{0}^{3} y^{2}\;dy
= \frac{1}{4}\left[\frac{y^{3}}{3}\right]_{0}^{3}
= \frac{1}{4}\cdot \frac{27}{3}
= \frac{9}{4}.
$$
Correct Answer: (B) $( \dfrac{9}{4} )$


